What Are Water Soluble Fertilizers and How Do They Work

You may ask, what are water soluble fertilizers? These fertilizers dissolve fully in water. This helps you give nutrients straight to plant roots. Water soluble fertilizers act fast. The nutrients are already mixed in the water. Plants can take them in right away. This quick action makes them liked by many growers. Both big farms and home gardeners use them. You can use them with drip irrigation. You can also use foliar feeding or a watering can.
Easy to mix and use
Good for many kinds of plants
Key Takeaways
Water soluble fertilizers mix fully in water. They give nutrients fast to plant roots or leaves. Plants can take in these nutrients quickly.
These fertilizers can be synthetic or organic. Each type has its own benefits. Some give nutrients fast. Others help the soil stay healthy.
You can use these fertilizers in many ways. Try drip irrigation, foliar feeding, or watering cans. This makes them useful for many plants and systems.
Using water soluble fertilizers helps plants grow strong. They give the right nutrition at each growth stage. This makes plants healthier.
Mix fertilizers with clean water. Follow the label instructions. Do not use too much. This keeps plants and the environment safe.
Watch for salt buildup in the soil. Salt can hurt plants. Use clean water and make sure the soil drains well. This helps stop salt problems.
Test your soil and water often. Check how healthy your plants are. Change how you use fertilizer to get the best results.
Keep fertilizers in a cool, dry place. Always check if products can be mixed before you combine them.
What Are Water Soluble Fertilizers

When you ask, "what are water soluble fertilizers," you want products that dissolve in water. This makes them different from other fertilizers. You mix them with water and give nutrients to plant roots or leaves. Plants take in these nutrients fast because they are already dissolved. This is why many farmers and gardeners like water soluble fertilizers.
Key Features
Water soluble fertilizers have some important traits:
High solubility: Nutrients like nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P₂O₅), and potassium (K₂O) dissolve in water.
Versatile forms: You can find them as liquids, powders, crystals, or granules.
Safe pH: Most solutions have a pH above 6. This helps stop equipment from rusting.
Clear appearance: Many solutions look clear and colorless. Some have colors because of their ingredients.
Precise nutrient content: Labels show the exact amount of each nutrient. This helps you manage plant nutrition easily.
Compatibility: These fertilizers work with many systems, like drip irrigation and foliar sprays.
Tip: Always check the pH and look at your fertilizer solution before using it. This helps you avoid equipment problems and gives even nutrients to plants.
Types
There are two main types of water soluble fertilizers: synthetic and organic.
Synthetic
Synthetic water soluble fertilizers are made by chemical processes. They are very pure and give nutrients quickly. These products often have a mix of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and trace elements. You can use them in fertigation, foliar feeding, and hydroponic systems. Synthetic fertilizers let you pick the right formula for your crops and their growth stage.
Organic
Organic water soluble fertilizers come from natural things. Fish-based fertilizers, liquid kelp, and compost teas are some examples. These give nutrients and also helpful microbes and organic matter. You might pick organic if you want better soil or want to be more eco-friendly. They are good for home gardens and special crops.
Common Examples
You can find many water soluble fertilizers in stores. Here are some popular ones:
NPK blends: These have nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in different amounts. They help plants grow and work for many crops.
Calcium nitrate: Gives calcium and nitrogen. These help make cell walls strong and boost growth.
Mono potassium phosphate (MKP): Has phosphorus and potassium. It is good for flowers and fruits.
Potassium nitrate: Gives potassium and nitrate nitrogen. It helps stems and leaves stay healthy.
Fish-based fertilizers: Give organic nitrogen and phosphorus. Some have extra potassium.
Liquid kelp/seaweed: Has trace elements and growth hormones. It helps roots grow and plants handle stress.
Compost tea: Gives micronutrients and helpful microbes for soil health.
Fertilizer Type | Main Nutrients | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
NPK Blends | N, P, K | General plant nutrition |
Calcium Nitrate | Ca, N | Fruit, vegetable crops |
Mono Potassium Phosphate | P, K | Flowering, fruiting plants |
Potassium Nitrate | K, N | Leafy greens, hydroponics |
Fish-Based | N, P (+K sometimes) | Organic gardening, soil health |
Liquid Kelp/Seaweed | Trace elements, K | Rooting, stress recovery |
Compost Tea | Micronutrients, microbes | Soil improvement, organic crops |
You can use water soluble fertilizers in different ways:
Fertigation: Put the fertilizer into your irrigation system. This gives nutrients to roots and helps plants grow.
Foliar feeding: Spray the nutrient solution on leaves. Plants take in nutrients fast. This helps fix problems or helps plants during stress.
Hydroponics: Use water soluble fertilizers to give all nutrients in soilless systems. You can control the amount for healthy plants.
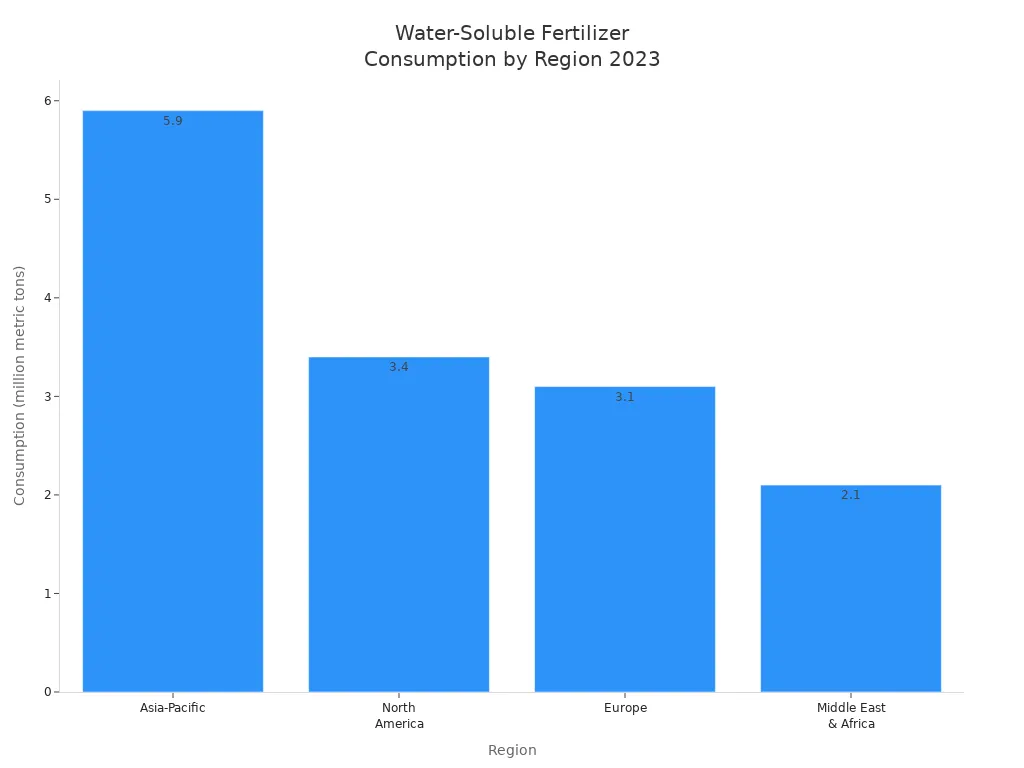
Water soluble fertilizers are used a lot in big farming areas. Asia-Pacific uses the most, then North America and Europe. Most are used for field crops, but more people use them for gardens and special crops now.
If you want quick results and control over plant nutrition, water soluble fertilizers are a good choice. You can pick from many products to fit your crops and growing needs.
How Water-Soluble Fertilizers Work
Dissolving in Water
When you use water-soluble fertilizers, you mix them with water first. These fertilizers dissolve fast and make a clear liquid. This happens quickly, especially with things like monoammonium phosphate (MAP) and diammonium phosphate (DAP). After they dissolve, the nutrients are ready for plant roots or leaves to take in.
Here is how it works:
You put the fertilizer in water. The nutrients break into ions.
These ions spread out in the water and make an even mix.
When you pour this mix on soil or spray it on leaves, the nutrients go right to the plant’s roots or leaves.
Plants can use these nutrients right away. They do not have to wait for the fertilizer to break down.
Note: How fast plants get nutrients depends on soil moisture, pH, and the kind of nutrient. For example, phosphorus can stick to clay or minerals in the soil, so it may move slower. Potassium can also get stuck in soil or wash away in sandy soils.
Remember, water-soluble fertilizers dissolve as ionic salts. This means nutrients are ready for plants almost right away. But things like pH, cation exchange capacity (CEC), and microbes in the soil can change how much nutrients your plants get.
Nutrient Uptake
Fast Absorption
Water-soluble fertilizers help plants by giving them nutrients fast. When you use these fertilizers, the nutrients move quickly in the soil water to the roots. The roots take them in almost at once. This quick action helps fix problems like low nitrogen, phosphorus, or potassium faster than other fertilizers.
You can see the good changes in your plants:
Leaves turn green and healthy if they were yellow from not enough nitrogen.
Roots grow stronger and deeper with more phosphorus.
Fruits and flowers grow better with extra potassium.
The water you use is important. Clean water with the right pH and not too many minerals helps plants take in nutrients easily. If the water has too many minerals or the wrong pH, plants may not get all the nutrients.
Comparison to Granular
You might wonder how water-soluble fertilizers are different from granular or slow-release fertilizers. The biggest difference is how fast they work and how well they give nutrients.
Fertilizer Type | Nutrient Availability | Nutrient Uptake Speed | Common Forms | Application Methods |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Water-Soluble Fertilizer | Fast nutrient absorption, high efficiency | Powder, liquid | Drip irrigation, foliar spray, fertigation | |
Granular Fertilizer | Nutrients release slowly into soil | Slower uptake, sustained release | Granular, powder | Soil application, base fertilization |
Granular fertilizers let nutrients out slowly as they break down. This slow release means plants may not get what they need right away. Water-soluble fertilizers give nutrients fast and evenly. This is helpful if your plants look weak or need a quick boost when growing.
Studies show that water-soluble fertilizers like urea-ammonium nitrate (UAN) take in water from air and soil faster than granular urea. This means plants get nutrients quicker, but there is a bigger chance of losing nutrients if the soil is dry. You should always pick the right fertilizer and way to use it for your crops and soil.
Tip: Use water-soluble fertilizers if you want fast results and to control nutrients closely. Pick granular fertilizers if you want a slow and steady supply of nutrients for a longer time.
Benefits
Quick Results
You want your plants to be strong and healthy. Water soluble fertilizers help you see changes fast. When you mix them with water, the nutrients dissolve quickly. Plants can take in these nutrients almost right away. You will notice greener leaves and stronger stems soon. Your plants will grow better in a short time. If your plants look weak, you can fix it fast with liquid fertilizers. These fertilizers send nutrients straight to the roots or leaves. You do not have to wait long to see results. This quick action makes liquid fertilizers popular for gardeners and farmers who need fast results.
Tip: Use water soluble fertilizers when your plants need a quick boost, like during flowering or after moving them.
Efficient Use
You want to use your supplies in a smart way. Water soluble fertilizers let you control how much nutrition your plants get. You can change the amount and timing for each growth stage. This helps you avoid giving too much or too little fertilizer. When you use liquid fertilizers with irrigation or sprays, you target the roots or leaves. This cuts down on waste and keeps nutrients where plants need them. Studies show these fertilizers help plants use nutrients better and give higher yields. You also help the environment by stopping extra nutrients from getting into water.
Nutrients reach roots fast.
You can make feeding plans for different crops.
Less fertilizer is wasted, so you save money.
You help the earth by stopping nutrient loss.
Versatile Application
You can use water soluble fertilizers in many ways. They work great in hydroponics, where plants grow in water with nutrients. For potted plants, you can pour liquid fertilizer on the soil or spray it on leaves. On lawns, these fertilizers help grass turn green and grow well. Liquid fertilizers mix easily with water and work with most irrigation systems, like drip or sprinklers. You can also change the nutrient mix for what your plants need at each stage.
Application Area | Benefit of Water Soluble Fertilizers |
|---|---|
Hydroponics | Exact control of nutrients for healthy plants |
Potted Plants | Fast delivery to roots or leaves in pots |
Lawns | Quick green color and better plant growth |
Note: Liquid fertilizers are flexible and easy to use, so they work for many plants and growing systems.
How to Use Water Soluble Fertilizers

Water soluble fertilizers let you feed plants in many ways. You can pick the best way for your garden or crops. The right method helps plants get what they need to grow strong.
Application Methods
Drip Irrigation
Drip irrigation is good for big gardens and farms. You mix fertilizer with water and send it through drip lines. This puts nutrients right at the plant roots. It saves water and stops waste. Make sure the fertilizer is fully dissolved so nothing blocks the system. Change the amount you use as your plants grow.
Foliar Feeding
Foliar feeding means spraying fertilizer on plant leaves. Plants take in nutrients fast through tiny holes called stomata. Use this if plants look weak or have poor roots. Spray early morning or late afternoon to keep leaves safe. Do not spray before rain or when the sun is strong.
Watering Can
A watering can works well for small gardens or pots. Mix fertilizer in water and pour it at the plant base. This is good for veggies, flowers, and young trees. Make sure the soil is wet before you add the mix. Water again after feeding to help nutrients reach the roots.
Tip: For big crops and fruit trees, try soil drenching. Mix fertilizer in water and pour it around the roots. Use low amounts to keep roots safe.
Mixing Tips
Mixing fertilizer the right way keeps plants healthy. Start with clean water that has no chlorine. Warm water helps fertilizer dissolve faster. Fill your bucket or tank about 70% before adding fertilizer. Add fertilizer slowly and stir until it is gone. Add more water to reach the final amount.
Stay under 80% of the fertilizer’s dissolving limit to stop clumps.
Do not mix fertilizers that do not work together, like calcium with phosphate or sulfate.
Always follow the label for how much to use and how often.
Keep leftover mix in closed containers away from sun, and use it within a month.
Note: Put fertilizer on wet soil. Dry soil can cause salt to build up and hurt roots.
Timing
When you feed plants matters for how well they use nutrients. Give water soluble fertilizers when plants are growing most. This is when they need more food for roots, flowers, and fruit. Early morning or late afternoon is best, especially for leaf sprays. Do not feed before heavy rain or nutrients may wash away.
Change your plan based on plant age and weather. Young plants need small, often feedings. Older plants may need bigger, less often feedings. Watch your plants for signs they need more or less food.
Growth Stage | Best Time to Feed Plants |
|---|---|
Seedling | Small, often feedings |
Vegetative Growth | Feed every 1-2 weeks |
Flowering/Fruiting | Give more potassium and phosphorus |
Dormant | Feed less or stop |
Watch your plants. Green leaves, strong stems, and good color mean your plan works.
Concerns
Salt Buildup
When you use water soluble fertilizers, you need to watch for salt buildup. Too much salt in the soil can hurt your plants and lower your harvest. Fertilizer salts can pile up around roots, especially if you use them a lot or if water does not drain well. This makes it hard for plants to get water and nutrients. Your plants might look weak, wilt, or have burned leaves.
Here is a table to help you see the risks and ways to handle them:
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Potential Risks of Salt Buildup | - Stops plants from taking in water and nutrients |
Types of Salt-affected Soils | 1. Saline soils: lots of salts, hard for plants to get water |
Mitigation Strategies | - Wash salts below roots with clean water |
Tip: Always test your soil and water for salt. Use clean water and make sure water drains well to stop salt problems.
Soil Health
You want your soil to be healthy so your plants grow strong. Using only synthetic water soluble fertilizers can hurt soil health after a while. These fertilizers do not add organic matter, which soil microbes need to live. If you use them too much, your soil may lose organic matter, have fewer good microbes, and get weaker.
Mixing organic and water soluble fertilizers helps soil keep carbon and supports microbes.
Adding compost or cover crops with fertilizer keeps soil balanced and healthy.
Too much chemical fertilizer can lower soil pH, hurt good bacteria, and make soil lose nutrients or wash away.
Healthy soil has the right mix of carbon and nitrogen. Try to keep the carbon to nitrogen ratio between 15:1 and 25:1.
Using organic matter with fertilizer helps soil hold water, store nutrients, and keep plants healthy.
Note: Change crops, add compost, and do not use too much fertilizer. These steps help your soil stay alive and work well.
Environmental Impact
Water soluble fertilizers can harm the environment if you do not use them right. If you use too much, rain or watering can wash nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus into rivers and lakes. This runoff can cause algae to grow fast, which lowers oxygen in water and hurts fish and other animals. In some places, like the U.S. Midwest, drainage pipes move fertilizer into rivers quickly, making water cleaning harder and raising health risks.
Phosphorus runoff from yards and farms can feed algae, making water dirty and unsafe. Some algae make toxins that kill fish and can make water dangerous for people and pets. Nitrogen from fertilizers can get into groundwater, causing health problems like "blue baby syndrome" in babies and even cancer.
You can help the environment by:
Using the right amount of fertilizer at the right time.
Picking slow-release or eco-friendly fertilizers that let out nutrients slowly and waste less.
Adding organic matter to soil to cut down on runoff.
Planting buffer strips or cover crops to catch nutrients before they reach water.
Modern fertilizers with special coatings can slow down how fast nutrients come out, help soil, and lower pollution. Many coatings break down safely in soil, so you can grow healthy plants and protect the earth.
🌱 Remember: Using fertilizer wisely keeps your plants, soil, and water safe and healthy.
Best Practices
Choosing Products
Picking the right water soluble fertilizer helps plants grow well. You need to choose a fertilizer that fits your water and plant needs. Water alkalinity can change how fertilizers work. Use the table below to help you decide:
Water Alkalinity (ppm CaCO3) | Fertilizer Acidity/Basicity | Acid Injection Needed |
|---|---|---|
Potential basicity 0-200 lb CaCO3/ton | No | |
60-120 | Potential acidity 0-200 lb CaCO3/ton | No |
120-180 | Potential acidity 300-400 lb CaCO3/ton | No |
180-250 | Potential acidity 400-600 lb CaCO3/ton | Maybe |
250+ | Adjust alkalinity with acid first | Yes |
If your water does not have enough calcium, magnesium, or sulfate, use different fertilizers or add extra nutrients. This stops your plants from missing important things they need. Switch between acidic and basic fertilizers to keep the pH balanced. Always check your water for sodium and chloride. Too much can hurt your plants and may mean you need to treat your water. Pick fertilizers that match what your plants need at each stage. Young plants need more nitrogen. Flowering plants need more phosphorus and potassium. Organic fertilizers like liquid kelp or fish-based types help soil and lower salt problems.
Tip: Test your water and soil before picking a fertilizer. This helps you avoid trouble and gives your plants the best chance to do well.
Reading Labels
Reading fertilizer labels helps you avoid mistakes and keeps plants safe. Labels tell you what nutrients are inside, like nitrogen, phosphate, and potash. This helps you pick the best one for your plants. Labels also say which plants the fertilizer works best for. This stops you from using the wrong kind on sensitive plants. Every label shows how much to use and how to use it. Follow these rules so you do not give too much and burn your plants. Mixing and timing instructions help you use the right amount. This matters for water soluble fertilizers because they work fast. Using too much can hurt your plants or pollute water.
Labels show what nutrients are in the fertilizer.
You can see which plants the fertilizer is for.
The label tells you how much and how to use it.
Mixing and timing tips help you not use too much.
Following the label keeps your plants and the earth safe.
Note: Start with a soil test and always follow the label. This keeps your plants healthy and stops waste.
Monitoring Plants
You need to watch your plants often to keep them healthy. Begin by checking your soil’s texture, pH, and nutrients. Think about your weather and the plants you grow. Use simple tools like soil test kits or high-tech tools like sensors and drones. These tools help you find problems early. You can see if your plants need more or less fertilizer. Sensors give you real-time data about how your plants react to feeding. Change your fertilizer plan if you see yellow leaves, slow growth, or other stress signs. Learn how to use your tools well. Keep learning about new ways to check plant health.
Use soil tests and sensors to check how plants are doing.
Watch for changes in leaf color, growth, and shape.
Change fertilizer use if you see problems.
Check your tools often to make sure they work right.
Learn about new tools for watching plants.
🌱 Healthy plants grow strong, have green leaves, and give good crops. Checking your plants often helps you find problems early and take care of them for the best results.
Water soluble fertilizers help your plants get nutrients fast and exactly when needed. You can use them in different ways and see results quickly. But you should always think about the good and bad sides before picking them. The table below shows the main things to think about:
Key Points to Consider | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
Nutrient Delivery Precision | You can feed plants just what they need at each stage | Too much can hurt plants and the environment |
Compatibility with Systems | Works with drip lines and other watering systems | You may need to buy and care for special tools |
Nutrient Absorption Speed | Plants react fast to these fertilizers | Effects do not last long, so you must use them often |
Application Versatility | You can use them in many ways: drip, spray, or soil | If you are not careful, nutrients can wash away |
Soil Health Impact | - | Too much salt can build up and hurt roots |
Best Practices | Mix carefully, test soil often, use with slow-release types | - |
For the best results, try these tips:
Mix the right amount and use the right amount each time.
Check your plants and soil often to spot problems early.
Feed plants when they are growing and when it is cool outside.
Keep fertilizers in a cool, dry spot.
If you use water soluble fertilizers the right way and pay attention, your plants can grow strong and healthy. You just need to watch for both the good and bad sides.
FAQ
What is the best way to store water soluble fertilizers?
Keep fertilizers in a cool and dry spot. Close the container tightly after each use. Do not let sunlight or water get in. This stops clumps and keeps nutrients good.
Can you mix different water soluble fertilizers together?
You can mix some fertilizers, but check if they work together first. Some nutrients can react and make clumps. Always read the label or ask someone who knows. Try mixing a small amount before using more.
How often should you apply water soluble fertilizers?
Most plants need food every one or two weeks when growing. Always look at the label for the right time. Change how often you feed based on your plant and its growth.
Are water soluble fertilizers safe for all plants?
Most plants can use water soluble fertilizers. Some plants are sensitive and need weaker mixes. Start with less and watch your plants for any problems.
What should you do if you see fertilizer burn on your plants?
Stop using fertilizer right away. Water the soil a lot to wash out extra salts. Cut off any leaves that look hurt. Wait until your plants look better before feeding again.
Can you use water soluble fertilizers in organic gardening?
You can use organic water soluble fertilizers like fish emulsion or compost tea. These help the soil and are good for organic gardens.
Do water soluble fertilizers expire?
Most water soluble fertilizers last a long time if you store them right. Heat or water can make them clump or not work as well. Always check if the color or texture has changed before using.
Tip: Always read the label and follow the steps to help your plants do their best.
See Also
Understanding How NPK Fertilizer With Humate Functions
Comparing Humic Acid And Seaweed Extract Fertilizers Benefits
Enhancing Pond Water Quality Using Sodium Humate Explained
