Exploring Macronutrient, Secondary Nutrient, and Trace Element Water Soluble Fertilizers
You use water-soluble fertilizers to give crops important nutrients very well. These fertilizers mix fast in water, so plants get nutrients quickly. You can use irrigation or foliar sprays to deliver them. There are three main types of these fertilizers: macronutrient, secondary nutrient, and trace element water soluble fertilizers. Knowing about these types helps you pick the right fertilizer for your plants. It also helps plants take in more nutrients. Michigan State University research shows water soluble fertilizer can give up to 95% nutrient uptake. This is much better than granular fertilizers. You get more choices, better root growth, and stronger plants when you pick the best fertilizer types.
Key Takeaways
Water-soluble fertilizers mix fully in water. They give nutrients to plants fast. You can use them with irrigation or foliar sprays.
There are three main types of these fertilizers. The first is macronutrient, called NPK. The second is secondary nutrient, like calcium, magnesium, and sulfur. The third is trace element, which has micronutrients like iron and zinc.
Using the right fertilizer type is important. Balanced nutrient ratios help plants grow strong. This also improves yield and keeps the environment safe.
Water-soluble fertilizers work well with drip irrigation. They are good for foliar application and fertigation too. These methods save water and cut down waste. They also help plants take in more nutrients.
Test your soil before using fertilizer. Match the fertilizer to what the crop needs. Also, think about the plant’s growth stage. This helps plants use nutrients better and stay healthy.
Follow best practices like the 4Rs. Use the right source, rate, time, and place. Calibrate your equipment to avoid losing nutrients. This also saves money.
Chelated micronutrient fertilizers help plants take in trace elements. They work well when soil conditions are tough.
Picking water-soluble fertilizers helps farming stay sustainable. It makes crops better, lowers pollution, and keeps soil healthy.
Water Soluble Fertilizer Basics
What Are Water-Soluble Fertilizers
Water-soluble fertilizers help crops get nutrients fast and easily. These fertilizers mix fully in water. You can give them to plants through irrigation or by spraying on leaves. They are different from regular solid fertilizers. Water-soluble fertilizers use pure ingredients and have many nutrients. They include NPK blends, secondary nutrients like calcium and magnesium, and chelated micronutrients. Some special types have amino acids or humic acids for certain crops.
Water-soluble fertilizers work quickly and let you control plant nutrition well.
Here is a table that compares different fertilizer types:
Fertilizer Type | Composition Characteristics | Functional Features and Uses |
|---|---|---|
Water-Soluble Fertilizers (WSFs) | Fully dissolve in water; very pure; have NPK, secondary nutrients, chelated micronutrients, additives | Give nutrients fast; work with fertigation and foliar feeding; easy to manage; less leaching; fit crop needs |
Traditional Solid Fertilizers | Do not fully dissolve; may release slowly | Nutrients come slower; less exact; not always good for fertigation; not as flexible |
Controlled-Release Water-Soluble | Dissolve but release slowly | Need less frequent fertigation; work better; less leaching |
Chelated Micronutrient Fertilizers | Micronutrients with chelating agents | Plants take in more nutrients; nutrients stay stable; good for precise micronutrient use |
Functional Additive Fertilizers | Have amino acids, humic acids, seaweed extracts | Help plant health, root growth, and nutrient uptake |
Key Benefits of Water Soluble Fertilizers
Water soluble fertilizers give many benefits to your crops. They help plants use nitrogen better, grow more, and lose fewer nutrients to the environment. You can match nutrients to what plants need at each growth stage. This makes plants healthier and harvests better. Some types release nutrients slowly, so you do not need to use them as often.
Plants use nutrients better because they absorb them fast.
Crops often grow more than with regular fertilizers.
You protect the environment by lowering nitrogen loss and gas emissions.
Some types help soil hold water and stay healthy.
Tip: Using water soluble fertilizer can help you get better results with less waste.
How Water Soluble Fertilizers Work
Water-soluble fertilizers mix fast in water. You can put them in irrigation systems or spray them on leaves. This sends nutrients right to roots or leaves, so plants take them in quickly. Studies show fast-dissolving fertilizers, like triple-super phosphate, help roots take up phosphorus faster. Early nutrient use helps crops grow strong and give high yields.
You can use water soluble fertilizers with drip or sprinkler irrigation. These systems spread nutrients evenly to all plants. This cuts waste and works better. To stop clogging, test if the fertilizer mixes well with your water using a jar test. Fertilizers that stay clear in water, like phosphoric acid-based ones, are best for drip systems.
Water-soluble fertilizers mix easily, so you can add them to irrigation lines.
This way, nutrients go right to the roots for best use.
You stop nutrient loss and make sure every plant gets enough.
Always check if the fertilizer works with your water to avoid clogs.
Note: The right water soluble fertilizer with your irrigation system saves time, water, and nutrients.
Macronutrient Water Soluble Fertilizers

Macronutrient water soluble fertilizers give crops the main nutrients. These fertilizers focus on three important elements. They are nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. People call these NPK water-soluble fertilizers. Each nutrient helps plants grow in a special way. Using the right NPK ratio gives you better crops and quality.
NPK Fertilizers
NPK water-soluble fertilizers have nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These nutrients dissolve fast in water. Plants can take them in quickly, especially when growing fast. You can pick different NPK ratios for your crop’s needs.
Nitrogen (N)
Nitrogen helps plants grow leaves and stems. It is the main nutrient for green growth. Using nitrogen fertilizer like urea or ammonium nitrate helps crops grow fast. Nitrogen also helps plants make protein and chlorophyll. Chlorophyll is needed for photosynthesis.
Phosphorus (P)
Phosphorus helps roots grow and makes flowers and fruit. It is important for moving energy inside the plant. Using water soluble fertilizers with phosphorus, like monoammonium phosphate or diammonium phosphate, helps crops start strong. Phosphorus also helps seeds form and makes your harvest better.
Potassium (K)
Potassium keeps plants healthy and helps them handle stress. It controls water in the plant and helps enzymes work. Potassium also makes fruit bigger, brighter, and tastier. Using potassium nitrate or sulfate of potash gives crops what they need for strong growth.
Common Forms of Macronutrient Fertilizers
There are many fertilizers that give these macronutrients. The table below lists some common water-soluble fertilizers used in farming:
Fertilizer Type | Macronutrient(s) | Form and Solubility | Usage/Application Details |
|---|---|---|---|
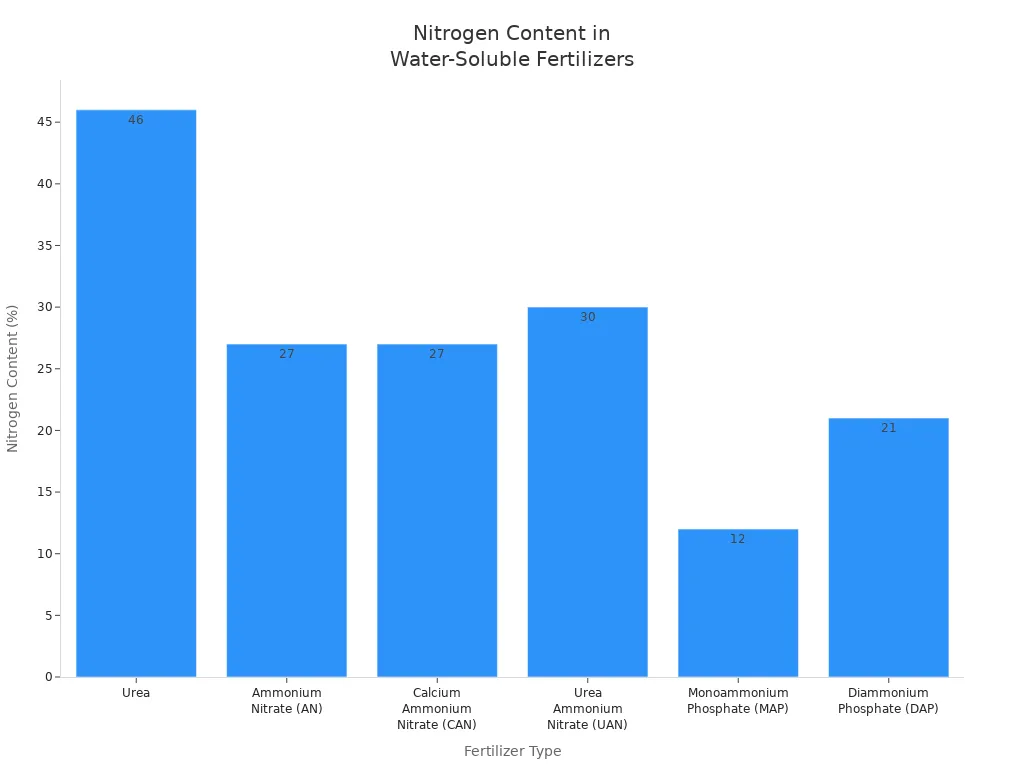
Urea | Nitrogen (46% N) | Solid, water-soluble | Most used nitrogen fertilizer; can be solid or dissolved; needs dry storage. |
Ammonium Nitrate (AN) | Nitrogen (26%-28% N) | Solid or dissolved in water | Used in mixes like CAN; can go in irrigation; must be handled safely. |
Calcium Ammonium Nitrate (CAN) | Nitrogen (26%-28% N) | Solid, stable material | Common mix; more stable and easier to use than pure AN. |
Urea Ammonium Nitrate (UAN) | Nitrogen (28/30/32%) | Liquid solution, water-soluble | Easy to use and mix with other fertilizers; good for irrigation; needs careful storage. |
Monoammonium Phosphate (MAP) | Phosphorus (62% P2O5), Nitrogen (12% N) | Solid or dissolved in water | Main phosphate source; stable; can be solid or used in irrigation. |
Diammonium Phosphate (DAP) | Phosphorus (54% P2O5), Nitrogen (21% N) | Solid or dissolved in water | Popular phosphate fertilizer; stable and easy to store; good for irrigation. |
You can also use potassium nitrate, mono potassium phosphate, urea phosphate, and sulfate of potash. These fertilizers dissolve well in water and work with most irrigation systems.
Tip: Pick the right water soluble fertilizer for your crop’s growth stage and soil.
Role in Plant Growth
Water soluble fertilizers with balanced NPK help crops grow strong. These fertilizers give plants what they need at the right time. This helps roots grow fast, stems get strong, and fruit or flowers grow better.
Water-soluble fertilizers dissolve fully, so plants get nutrients fast.
They help plants grow quickly, especially when making flowers or fruit.
You can use them with irrigation, which saves time and spreads nutrients evenly.
Balanced macronutrients give better yield and quality and cut waste.
Field tests show balanced NPK water-soluble fertilizers can raise yield and use fertilizer better. For example, using a balanced NPK ratio with some fulvic acid lets you use less nitrogen but still get good yields. This means you use less fertilizer and get better results.
Yield Impact | Quality Impact | Environmental Impact | Economic Benefit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
N0.3 P0.2 K0.3 | Moderate yield | High fruit quality | Low pollution risk | Slight increase from better quality and less input |
N0.6 P0.3 K0.15 | Big improvement | Big improvement | Not given | Not given |
Higher than recommended | Highest yield | Lower quality | More pollution risk | Lower benefit because of higher cost |
Always match the NPK ratio to your crop’s needs. Too much nitrogen can lower fruit quality and cause more pollution. Too little phosphorus or potassium can slow growth and lower yield.
Studies show chloride, as a macronutrient, helps crops use water better and grow bigger leaves. Crops like wheat and coconut need more chloride for healthy growth. Using the right fertilizers, including those with chloride, helps plants grow strong.
Note: Balanced macronutrients from water soluble fertilizers give crops the best chance for healthy, high-quality growth.
Secondary Nutrient Water Soluble Fertilizers
Secondary nutrient water soluble fertilizers give crops more nutrients than just NPK. These fertilizers focus on calcium, magnesium, and sulfur. Plants need these nutrients to grow well and stay strong. They help build tough cell walls and help plants handle stress. Using the right fertilizer types stops common plant problems and helps you get more crops.
Calcium, Magnesium, and Sulfur
Calcium (Ca)
Calcium helps make strong cell walls and keeps plant tissues firm. Plants need calcium to grow fruit and avoid problems like blossom end rot in tomatoes or bitter pit in apples. Calcium nitrate is a special water-soluble fertilizer. It gives plants both calcium and nitrogen that they can use right away.
Calcium nitrate gives calcium for strong cell walls.
It also gives nitrate nitrogen for leafy growth and helps plants take in other nutrients.
This fertilizer dissolves fast, so you can use it in irrigation or spray it on leaves.
You need to use it often because calcium does not move easily inside plants.
This stops calcium and nitrogen shortages, which can cause slow growth and bad fruit.
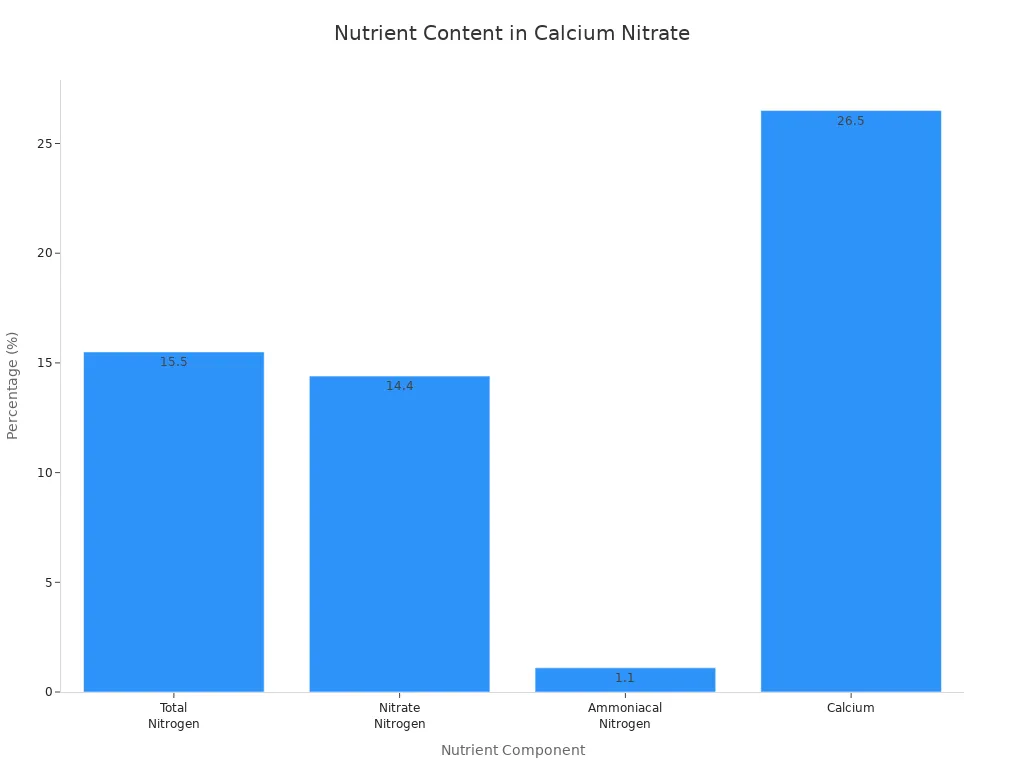
Nutrient Component | Percentage / ppm | Role in Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Functionality |
|---|---|---|
Total Nitrogen (N) | Helps plants make food and grow. | |
Nitrate Nitrogen | 14.4% (144,000 ppm) | Moves fast in soil and roots take it up quickly. |
Ammoniacal Nitrogen | 1.1% (11,000 ppm) | Works with nitrate nitrogen for balanced nutrition. |
Calcium (Ca) | 26.5% (265,000 ppm) | Builds cell walls, helps enzymes, and fights disease. |
Tip: Use calcium nitrate for fruiting crops to get more fruit, better quality, and stop common problems.
Magnesium (Mg)
Magnesium is in chlorophyll, which makes plants green and lets them use sunlight. If plants do not get enough magnesium, leaves turn yellow and growth slows. Magnesium also helps enzymes work and moves phosphorus inside the plant. You can use magnesium sulfate as a water soluble fertilizer to fix magnesium problems fast.
Sulfur (S)
Sulfur helps plants make proteins, vitamins, and enzymes. It also makes crops like onions and garlic taste and smell better. Sulfur works with nitrogen to help plants grow strong. If plants do not get enough sulfur, they look pale and weak. You can use water soluble fertilizers like ammonium sulfate or potassium sulfate to give plants sulfur.
Common Secondary Nutrient Fertilizers
You can pick from many secondary nutrient fertilizers. These water soluble fertilizers dissolve fast and work well with irrigation.
Fertilizer Type | Main Nutrient(s) | Application Method | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
Calcium Nitrate | Calcium, Nitrogen | Irrigation, Leaf Spray | Stops blossom end rot, makes fruit better |
Magnesium Sulfate | Magnesium, Sulfur | Soil, Leaf Spray | Fixes magnesium shortage, helps enzymes |
Ammonium Sulfate | Nitrogen, Sulfur | Soil, Irrigation | Gives sulfur and nitrogen together |
Potassium Sulfate | Potassium, Sulfur | Soil, Irrigation | Adds potassium and sulfur, makes crops taste better |
Note: Always choose the fertilizer that fits your crop’s needs and growth stage.
Benefits for Plant Health
Secondary nutrient fertilizers help plants in many ways. Plants need these nutrients to grow strong, fight stress, and give good harvests.
Calcium makes cell walls strong and helps fix damaged parts.
Magnesium helps plants use sunlight and phosphorus.
Sulfur helps make proteins and helps plants fight disease.
Water soluble fertilizers with secondary nutrients help crops handle dry weather, salty soil, and other problems. Phosphorus, often used as a secondary nutrient, helps plants use sunlight, water, and enzymes. It also helps plants survive hard times by making them stronger and helping them use water better.
Balanced nutrition, with secondary nutrients, keeps plants healthy and growing well.
Secondary nutrients work with macronutrients. When you give both, plants take in nutrients better and grow stronger. Mycorrhizal fungi in soil help plants get both macronutrients and secondary nutrients, so fertilizer works better. If you spray leaves with iron, copper, manganese, or zinc, you help plants grow and fight disease.
You need to keep all nutrients balanced. Too much phosphorus can stop plants from taking in iron. The right mix helps plants handle stress and grow well. Using the right water soluble fertilizers makes sure your crops get everything they need to do their best.
Trace Element Water Soluble Fertilizers
Trace element water soluble fertilizers give crops important micronutrients. Plants only need these in tiny amounts. But they are still very important for plant health. These fertilizers stop hidden hunger in plants. Hidden hunger means plants look fine but do not grow well. Even if you use enough macronutrients and secondary nutrients, plants can still lack micronutrients. You can use these fertilizers with irrigation, by spraying on leaves, or in hydroponics. This helps crops get the right mix of nutrients.
Essential Micronutrients
Plants need several micronutrients to stay healthy. Even though plants need just a little, these nutrients do a lot. The main micronutrients in water soluble fertilizers are iron, manganese, zinc, copper, molybdenum, and boron.
Micronutrient | Role/Function |
|---|---|
Zinc (Zn) | Helps plants grow and stops diseases from lack of zinc |
Manganese (Mn) | Helps plants grow and make flowers and fruit |
Iron (Fe) | Needed for plant energy and making green leaves |
Boron (B) | Helps build cell walls and make flowers and fruit |
Copper (Cu) | Needed for photosynthesis and enzyme work |
Molybdenum (Mo) | Helps plants use nitrogen and enzymes work |
Iron (Fe)
Iron helps plants make green leaves. It lets plants use sunlight for energy. If plants do not get enough iron, leaves turn yellow and plants grow slowly.
Manganese (Mn)
Manganese helps plants use sunlight and other nutrients. It also helps plants make flowers and fruit.
Zinc (Zn)
Zinc helps plants make hormones and enzymes. It helps plants grow strong stems and leaves.
Copper (Cu)
Copper helps enzymes work and helps plants use sunlight. It also helps plants fight disease.
Molybdenum (Mo)
Molybdenum helps plants use nitrogen. It lets plants take nitrogen from the air and grow well.
Boron (B)
Boron helps make strong cell walls. It also helps plants make flowers and fruit. Without enough boron, plants may have weak stems and poor fruit.
Chelated Micronutrient Fertilizers
Chelated micronutrient fertilizers use special molecules to wrap around metals like iron, zinc, and copper. This keeps the nutrients ready for plants to use. It works even if the soil has high pH or lots of calcium. Plants can take in these nutrients better and faster. Some common chelated types are:
Iron (Fe): Chelated iron helps plants stay green and healthy.
Zinc (Zn): Chelated zinc helps plants grow and take in nutrients.
Copper (Cu): Chelated copper helps enzymes work and plants grow well.
Manganese (Mn): Chelated manganese helps plants use sunlight and make hormones.
Chelated fertilizers work well in soil or as sprays on leaves. They stay dissolved and ready for plants to use. Spraying leaves with chelated micronutrients gives fast results. It helps fix problems quickly.
Tip: Use chelated micronutrient fertilizers if your soil has high pH or if you see signs of nutrient problems. This helps your crops get what they need to grow well.
Preventing Deficiencies
Many crops do not get enough trace elements like iron, zinc, or boron. This can cause yellow leaves, slow growth, and low harvests. Water soluble fertilizers with chelated micronutrients help stop and fix these problems. You can use them with irrigation or spray them on leaves for quick help.
Not enough iron makes leaves turn yellow between the veins. Use iron-rich water soluble fertilizers to fix this.
If plants do not get enough zinc or manganese, they may not grow well or make good fruit. Chelated forms in fertilizers help plants take in these nutrients and stop these problems.
Boron and molybdenum are also important. Without them, plants may have weak stems and poor flowers.
You can pick from many water soluble fertilizers made to fix certain problems. Products like Nova FINISH and Agrolution pHLow give fully chelated micronutrients for easy use. Acidifying fertilizers like Nova PeKacid keep nutrients dissolved and stop clogs in irrigation.
Note: Using trace element water soluble fertilizers often keeps crops healthy, gives better harvests, and makes sure plants get all the nutrients they need to grow strong.
Application Methods for Water Soluble Fertilizers

Drip Irrigation
Drip irrigation sends water-soluble fertilizers right to plant roots. It uses tubes and small outlets to put water and nutrients in the soil. This helps plants grow more and use water and nitrogen better. You do not need to visit the field as much, so you save time and work. Drip irrigation also keeps water away from weeds and lowers the chance of polluting groundwater.
But you need to buy things like tanks, injectors, and valves. You must check the system often to keep it working well. Emitters can get blocked if the water is not clean or the fertilizer is wrong. Pick fertilizers with a neutral pH and low salt index to stop clogs.
Tip: Flush your drip system often and use the right fertilizers to keep it working well.
Foliar Application
Foliar application means spraying water-soluble fertilizers on plant leaves. Plants take in nutrients fast through their leaves. This helps when plants are growing fast or roots cannot get enough nutrients. It works best for micronutrients like iron, zinc, and boron.
Studies show foliar feeding works quickly. For example, cotton plants take in 30% of sprayed nitrogen in one hour. Indian mustard grows better and makes better seeds when you spray boron and urea at flowering. Foliar calcium helps peanuts grow stronger and gives more peanuts. You can also use foliar sprays to fix hidden hunger in plants.
Crop | Fertilizer Type | Key Effects |
|---|---|---|
Cotton | Foliar-applied nitrogen (urea) | Fast absorption and moves to other parts |
Indian Mustard | Foliar B and N mixtures | Better growth, seed oil, and yield |
Soybean | Foliar boron (B) | Changes seed protein and sugar |
Peanut | Sorbitol-chelated calcium (Ca) | More calcium taken in and higher yield |
Safflower | Foliar-applied nano SiO₂ | Better germination, growth, and yield |
Spray at the right time and use the right amount. Too much fertilizer or spraying when it is hot can burn leaves. Foliar feeding should help soil fertilizing, not replace it.
Fertigation
Fertigation mixes fertilizer with irrigation water. This sends nutrients right to the roots. You can control when and how much fertilizer plants get. This helps match nutrients to what plants need and cuts waste.
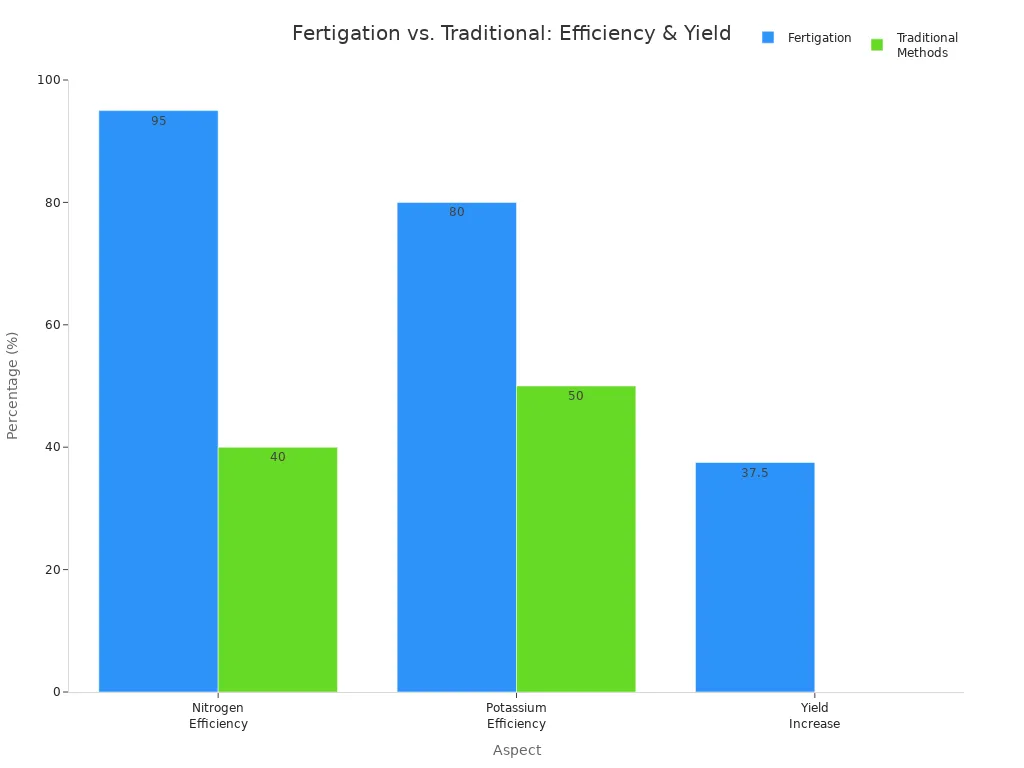
Fertigation stops nutrients from washing away. You use less fertilizer and water, so you save money and help the environment. Crops can grow 25–50% more with fertigation than with old ways. Leaves stay dry, so plants get fewer diseases.
Aspect | Fertigation Benefits | Traditional Methods |
|---|---|---|
Nutrient Delivery | Direct and steady to roots | Changes in soil |
Nutrient Loss Reduction | Less runoff and leaching | More nutrients lost |
Fertilizer Efficiency | Nitrogen up to 95%, Potassium ~80% | Nitrogen 30–50%, Potassium ~50% |
Crop Yield Improvement | Fewer crops | |
Water and Labor Savings | Uses less water and work | Needs more water and work |
Disease and Pest Management | Leaves stay dry | Leaves may get wet |
Control Over Application | Exact timing and amount | Not as exact |
Note: Test your soil and plants to make your fertigation plan work best.
Best Practices
Using water-soluble fertilizers the right way helps crops grow well. You can follow some simple steps to help plants use nutrients and waste less. Here are some best practices for your fertilizer plan:
Follow the 4Rs of nutrient stewardship: Pick the right fertilizer, use the right amount, apply it at the right time, and put it in the right spot. This helps you give your crops what they need and keeps the environment safe.
Test your soil regularly: Soil tests tell you what nutrients are already in your soil. Use this information to pick the best fertilizer and how much to use.
Develop a nutrient management plan: Work with an expert to make a plan for your field. The plan should think about your soil, crop, and weather.
Split your fertilizer applications: Do not use all the fertilizer at once. Give smaller amounts at different times. This helps plants get nutrients when they need them and stops waste.
Calibrate your equipment: Make sure your irrigation and sprayers give the right amount of fertilizer. This stops you from using too much or too little.
Use the right application method: Put fertilizer in the soil or use bands if you can. These ways help roots find nutrients and stop runoff.
Manage irrigation carefully: Only water as much as needed. Too much water can wash away nutrients. Too little water can keep plants from taking up nutrients.
Consider inhibitors: Use special products with nitrogen fertilizers. These slow down nitrogen loss and help more reach your crops.
Adjust for local conditions: Every field is different. Check your soil, crop, and weather. Change your fertilizer plan if you need to.
Tip: Always add fertilizer when crops are growing fast. Plants take in nutrients best during active growth.
You can use a simple table to keep track of your best practices:
Practice | Why It Matters | How Often |
|---|---|---|
Soil Testing | Finds nutrient gaps | Every 1–2 years |
Equipment Calibration | Ensures accurate delivery | Before each season |
Split Applications | Matches crop needs, reduces loss | At key growth stages |
Nutrient Management Plan | Customizes fertilizer use | Review yearly |
If you follow these best practices, your crops will grow better. You will protect the environment and use your resources well. You also lower the chance of losing nutrients and save money by using only what your plants need. Remember, careful fertilizer use means healthier plants and bigger harvests.
Choosing the Right Water Soluble Fertilizer
Assessing Crop and Soil Needs
Start by testing your soil before picking a water-soluble fertilizer. Soil tests show what nutrients are in your soil and what is missing. This helps you not use too much or too little fertilizer. You can then pick a fertilizer that fits what your soil and plants need.
Here are some simple steps to help you choose:
Test your soil to check nutrients and pH.
Find out what your crop needs to grow well.
Pick organic or inorganic fertilizer based on your goals.
Decide if you want a complete fertilizer or one for a certain nutrient.
Match the fertilizer’s nutrients to your soil test.
Think about when and how you will use the fertilizer.
Check your soil’s moisture, texture, and how nutrients move.
Look at your crop’s roots and growth stage to plan when to apply.
Do not use too much fertilizer to keep plants and the environment safe.
Tip: Remember the 4Rs—right source, right rate, right time, and right place. This helps you use fertilizer well and give your crops what they need.
Soil tests also help you keep pH balanced. If your water is alkaline, you may need a fertilizer that lowers pH. If your water is acidic, pick a fertilizer that raises pH. Keeping pH right helps plants grow strong and take in nutrients.
Understanding Fertilizer Labels
Reading fertilizer labels helps you make good choices. Each label has three numbers like 20-10-20. These numbers show nitrogen, phosphate, and potash. Labels also list secondary nutrients and micronutrients.
Look for these things on the label:
The N-P-K ratio for main nutrients.
All nutrients listed, including micronutrients.
What kind of nitrogen is in the fertilizer.
How the fertilizer changes soil pH.
How well it dissolves in water.
How much to use and safety rules.
Check the “Derived from” part to see where nutrients come from. Some labels show if the fertilizer will change your soil’s pH. For example, high ammoniacal nitrogen can lower pH. This can help or hurt your crop, depending on what it needs.
Note: Knowing these facts helps you pick a fertilizer that fits your soil, water, and crop for the best growth.
Matching Fertilizer to Growth Stage
Your crop needs different nutrients as it grows. When plants are seedlings, they need balanced nutrients for roots. In the vegetative stage, they need more nitrogen for leaves and stems. When plants flower or make fruit, they need more phosphorus and potassium.
You can use different NPK ratios for each stage:
Growth Stage | Nutrient Focus | Example NPK Ratio |
|---|---|---|
Seedling | Balanced nutrients | 10-10-10 |
Vegetative | Higher nitrogen | 20-10-10 |
Flowering/Fruiting | More P and K | 10-20-20 |
Change your fertilizer plan as your crop grows. This helps you give the right nutrients at the right time. You get better harvests and healthier plants. Always check your soil test before making changes.
Callout: Using the right fertilizer for each growth stage helps plants grow strong roots, green leaves, and good fruit.
Environmental and Economic Factors
When picking a water-soluble fertilizer, you should think about the environment and your money. Your choice affects your crops and the land, water, and air near your farm. Regular fertilizers can hurt the environment in many ways. They might change the soil’s pH and cause too much or too little of some nutrients. When it rains, these fertilizers can wash into rivers and lakes. This runoff pollutes water and causes algae to grow too much. Algae blooms can make dead zones where fish and other animals cannot live. These problems happen in places like the Gulf of Mexico. Regular fertilizers also let out gases like nitrous oxide. These gases make climate change worse. Over time, these problems can make your soil less healthy and lower the number of plants and animals in your fields.
Water-soluble fertilizers help stop many of these problems. They let you give plants the right nutrients at the right time. This means less fertilizer washes away or turns into gas. You use nutrients better, so less gets into the environment. Some water-soluble fertilizers have special coatings that break down on their own. These coatings control how fast plants get nutrients and help keep soil healthy. Using these fertilizers helps protect water, lower greenhouse gases, and keep soil good for future crops.
Tip: Water-soluble fertilizers help you grow crops and protect the environment for the future.
But you also need to think about cost. Water-soluble and controlled-release fertilizers usually cost a lot more than regular ones. Sometimes, they can cost two to eight times as much. The higher price is because of the special coatings and how they are made. Many farmers use them only for crops that make more money, like fruits, vegetables, or flowers. If you grow crops that do not sell for much, the extra cost may not be worth it.
Here is a simple comparison:
Fertilizer Type | Environmental Impact | Cost (per unit) | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
Conventional | High pollution risk | Low | Big fields, low-value |
Water-Soluble/Controlled-Release | Low pollution, better soil health | High | High-value, special |
You should think about the good and bad points before you choose. If you want to help the environment and grow crops that sell for more, water-soluble fertilizers are a good choice. If you need to save money, you might use these fertilizers only where they help the most.
Benefits of Balanced Fertilizer Use
Improved Plant Health
When you use balanced water-soluble fertilizers, plants grow stronger. Each nutrient helps plants in a different way. Nitrogen makes leaves green and full. Phosphorus helps roots and flowers grow well. Potassium helps plants fight stress and sickness. Secondary nutrients like calcium and magnesium make cell walls firm. They also help plants use water better. Micronutrients such as iron and zinc stop hidden hunger. This means plants do not look weak or sick.
A balanced plan gives crops all they need. You see fewer yellow leaves, weak stems, or bad fruit. Healthy plants fight bugs and disease more easily. They also get better after stress from heat or drought. Giving the right nutrients at the right time helps plants grow their best.
Healthy plants need balanced nutrition. Give crops what they need, and you will get better growth and more harvest.
Efficient Nutrient Uptake
Balanced fertilizer use helps plants use nutrients better. When you match fertilizer to your crop’s needs, plants take in more and waste less. Water-soluble fertilizers dissolve fast, so roots get nutrients right away. This lowers the chance of nutrients washing away or getting lost.
You can use special ways like fertigation or foliar sprays. These send nutrients right where plants need them most. This stops you from using too much fertilizer and keeps nutrients ready for crops. You also help the environment by cutting down runoff and pollution.
Using water and fertilizers the right way fixes old problems.
Giving the right nutrients and caring for soil makes crops better.
Good soil helps plants get more nutrients.
Adding organic matter and microbes makes soil hold water better.
These steps help you get more from every bit of fertilizer. Your crops grow better, and you save money by using less over time.
Sustainable Agriculture
Balanced fertilizer use helps farming stay healthy for the future. You protect soil, water, and air when you use fertilizer the right way. Mixing mineral and organic fertilizers keeps soil strong and improves how it feels. This also helps tiny living things in soil, so plants get more nutrients.
You lower harm to the environment by losing fewer nutrients and using less chemicals. Better soil gives you bigger harvests and better crops. You also save resources for people in the future.
Using water-soluble fertilizers the right way helps plants use nutrients and grow more.
Using both types of fertilizer keeps soil good and helps crops for many years.
Mixing nutrients well cuts pollution and lowers the need for chemicals.
Better soil means better crops and higher quality.
By picking balanced fertilizer plans, you help farming last longer. You grow more food, protect nature, and help your community stay healthy.
Smart fertilizer choices help farming and the planet. Make every use count for your crops and the earth.
You now know about macronutrient, secondary nutrient, and trace element water-soluble fertilizers. Each one helps plants in its own way. Pick your fertilizer by looking at what your crop and soil need. This gives you the best results.
Check your soil before using any fertilizer.
Use good habits for balanced nutrition and smart application.
Choose your fertilizer wisely. This helps farming stay healthy and lets your crops grow well for a long time.
FAQ
What makes water-soluble fertilizers different from regular fertilizers?
Water-soluble fertilizers mix fully in water. You can use them with irrigation or spray on leaves. Plants get nutrients fast this way. Regular fertilizers do not always dissolve well. They give nutrients slowly over time.
Can you mix water-soluble fertilizers with pesticides?
You can usually mix these fertilizers with many pesticides. Always read the label and do a jar test first. This helps stop clogs or bad reactions in your sprayer.
How often should you apply water-soluble fertilizers?
Apply water-soluble fertilizers every one or two weeks when plants grow fast. Change how often you use them based on your crop and soil tests. Using too much can hurt plants or waste nutrients.
Are water-soluble fertilizers safe for all crops?
Most crops do well with water-soluble fertilizers. You need to pick the right formula for your crop and its growth stage. Some crops are sensitive and need weaker mixes. Always follow the label for safe use.
What is the best way to store water-soluble fertilizers?
Keep water-soluble fertilizers in a cool, dry spot. Close the container tightly after each use. If they get wet, they may clump or not work as well. Always keep them away from kids and pets.
Do water-soluble fertilizers work in organic farming?
Most water-soluble fertilizers are made from synthetic materials. Some types, like fish emulsion or seaweed extracts, are okay for organic farms. Always check if the product is certified organic before using it.
How do you know if your plants need micronutrient fertilizers?
Watch for yellow leaves, slow growth, or weak stems. Soil and plant tests give the best answers. You can use chelated micronutrient fertilizers to fix these problems.
Can you use water-soluble fertilizers in hydroponics?
You can use water-soluble fertilizers in hydroponic setups. They give plants the right nutrients and dissolve fully in water. Always check and adjust nutrient levels for healthy plants.
See Also
How Water Soluble Fertilizers Function And Their Benefits
Comparing Humic Acid And Seaweed Extract Fertilizers Benefits
How Humic Acid Fertilizers Manage Nutrients For Sustainable Farming
The Role Of Humic Substances In Soil Health And Growth
Differences Between Biochemical And Mineral Forms Of Fulvic Acid
