How Sodium Humate Works As Additive For Paper, Leather, And Wood Stain Dyeing?

Sodium humate is a useful organic compound. It mostly comes from weathered coal, peat, and lignite. Many industries like sodium humate. It helps dyes spread better and makes colors look nicer in paper, leather, and wood stain. Manufacturers use it as a mordant and dispersant. This helps dyes spread evenly and makes products look better. The global market for sodium humate is growing. This is because it has special features and many uses.
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Global Market Size (2024) | |
Projected Market Size (2030) | USD 43 million |
Key Raw Materials | Weathered coal, peat, lignite |
Major Consuming Sectors | Construction, agriculture, paper, leather |
Key Takeaways
Sodium humate helps dye spread better and look brighter on paper, leather, and wood stains. It makes paper stronger by acting like glue. This makes the paper last longer and feel smoother for printing. Sodium humate also helps take out heavy metals from water. This keeps factory water clean and safe. Using sodium humate saves money on chemicals. It also means factories use fewer harsh additives. Sodium humate is safe for workers and the environment. It is non-toxic and eco-friendly. In leather dyeing, sodium humate helps colors look even. It also makes the process faster and better. For wood stains, it gives a rich, natural color. The color goes deep and helps protect the wood. Factories should test sodium humate first. This is because quality can change and colors might look different.
Sodium Humate
Definition
Sodium humate comes from things like weathered coal, peat, and lignite. People make it by getting humic acid from these materials. Then, they mix it with sodium hydroxide. This makes a sodium salt that can dissolve in water. Many industries use sodium humate because it helps dyes and chemicals work better. It looks like a black powder, flake, or granule. This makes it simple to use and mix with other things.
Chemical Nature
Sodium humate forms when humic acid loses hydrogen ions. These ions are replaced by sodium ions. This makes a molecule with a negative charge. It mixes well with water and other chemicals. Natural humic acid does not dissolve in water if the pH is low. But sodium humate stays dissolved in alkaline conditions. Its structure has both aliphatic and aromatic parts. This makes it complex and different each time. It also has groups like carboxyl and phenolic hydroxyl. These help it make strong bonds with metal ions. This is why sodium humate is special and useful in factories.
Sodium humate is the sodium salt of humic acid, which is made of large organic compounds.
It has groups called carboxyl and phenolic hydroxyl.
It dissolves well in water when the pH is alkaline because it is an ionic salt.
Its structure can change based on where it comes from and how it is made.
Key Properties
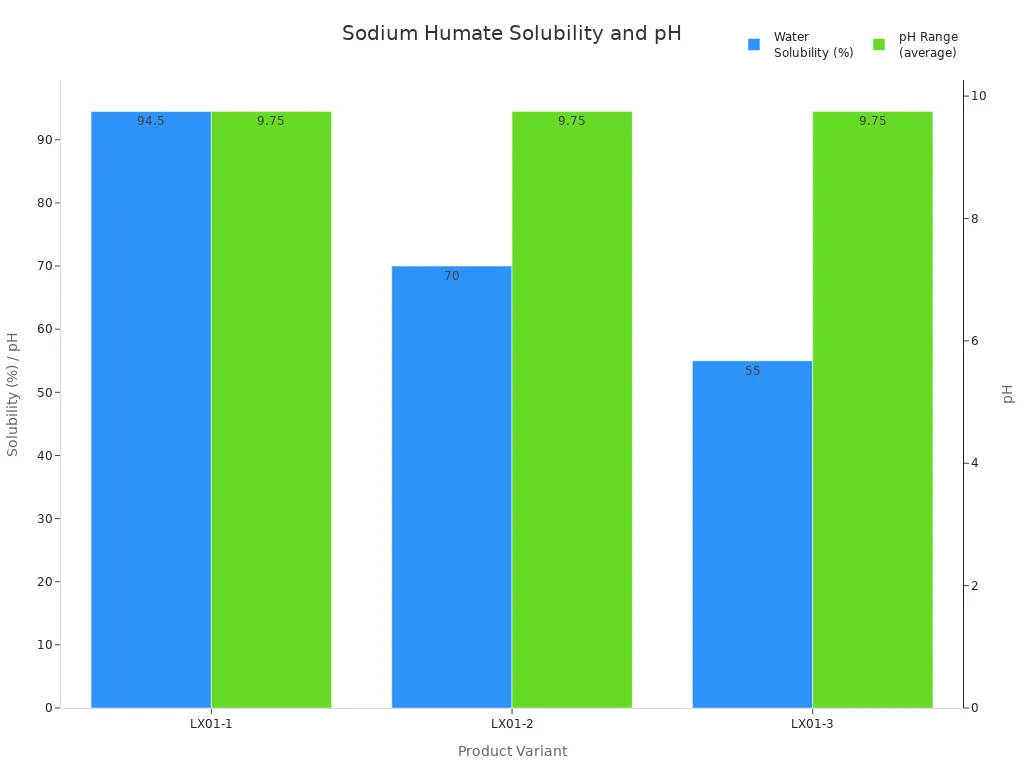
Sodium humate is known for being very soluble and alkaline. Most types dissolve in water from 75% to 100%. The pH is usually between 9 and 11. This helps it spread evenly in dyeing and water treatment. Sodium humate is safe because it is non-toxic, has no smell, and does not cause rust. This keeps workers and the environment safe.
Grade/Form | Water Solubility (%) | pH Range | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|
Various grades | 75% to 100% | 9 to 11 | Black flake/powder/granule |
Sodium humate can grab and hold onto heavy metal ions. Its carboxyl and hydroxy groups help catch metals like mercury from water. This makes it good for cleaning water and the environment. It has a high molecular weight, often over 70 kDa, which helps it bind metals better. These features make sodium humate helpful in paper, leather, and wood stain work. It makes colors brighter, products stronger, and helps keep things safe for nature.
Additive Mechanism
Industrial Action
Sodium humate is a strong additive in many factories. It grabs onto dyes, metals, and other chemicals. This happens through adsorption and desorption. Sodium humate can hold things and let them go later. In paper, leather, and wood stain dyeing, this helps control how dyes stick. This makes colors even and products look better.
Factories like sodium humate because it works with many materials. Its structure has many active spots. These spots help it grab and let go of dyes and metals. For example, in paper making, sodium humate catches heavy metals and takes them out of water. In leather dyeing, it helps dyes stick to fibers and then lets them go for a smooth look. Wood stain makers use it to help color spread and go deep into the wood.
Note: Sodium humate can manage adsorption and desorption well. It works with different pH levels and many dyes and chemicals.
Benefits
Sodium humate gives many good benefits as an additive. Its special adsorption and desorption help save money and work better in factories.
Cost Benefits:
Companies save money by using sodium humate. It means they need fewer costly chemicals. It can lower production costs by about 10%. It also cuts down on surfactants and stops ammonia loss. This makes work more efficient.Performance Benefits:
Sodium humate is a multifunctional polymer. Its strong adsorption and desorption help remove bad stuff and heavy metals from water. This makes products cleaner and work safer. In dyeing, it keeps colors bright and lasting. It also makes paper, leather, and wood stronger and better.Environmental Impact:
Sodium humate helps the environment. It lowers ammonia emissions and pollution by needing fewer harsh chemicals. Its adsorption and desorption trap and remove harmful things. This makes water treatment greener. The compound is natural and safe. It helps factories use less synthetic additives.Health and Productivity:
Studies show sodium humate makes water better and helps animals stay healthy in aquaculture. It helps animals grow and boosts their immune systems. These good things also help other industries. Sodium humate helps make safer and greener products.
Benefit Area | Description |
|---|---|
Cost | Lowers chemical use, reduces production costs, and improves efficiency |
Performance | Enhances dye uptake, product strength, and pollutant removal |
Environmental | Decreases emissions, supports green water treatment, and is eco-friendly |
Health/Productivity | Improves water quality and supports animal and worker health |
Tip: Manufacturers pick sodium humate for its strong adsorption and desorption. These features help them reach quality and environmental goals.
Paper Applications

Dyeing Agent
Paper makers use sodium humate to help color paper. It lets dyes spread out evenly on the paper. This works best when the pH is high. Other additives may not work as well in these conditions. In making cigarette paper, sodium humate helps keep the color even. It stops spots from forming. Sodium humate can grab dye molecules and then let them go slowly. This makes the color bright and the same everywhere. Factories also use sodium humate to test how well paper can take in methylene blue dye. This shows if the paper can hold and keep dyes.
Tip: Smooth color and even dyeing matter a lot for special papers used in packaging and printing.
Binder Role
Sodium humate also helps make paper stronger. It acts like glue and holds the fibers together. This makes the paper harder to tear or fold. It also makes the surface smoother. This helps when printing on the paper. Sodium humate can stick to both fibers and fillers. This gives the paper a better surface and helps ink stay on. When factories use sodium humate, the coating sticks better. This makes the paper higher quality and meets tough rules.
Makes paper stronger and last longer
Gives a smoother surface for good printing
Helps coatings stick better in finishing
Water Treatment
Good water is important for making paper. Sodium humate helps clean the water used in factories. It can grab heavy metals like copper, nickel, and lead. These metals are then taken out of the water. Tests show sodium humate can remove a lot of copper from water. It can take out up to 299 mg/L of copper ions. Other similar compounds can remove most metals in less than 30 minutes. This keeps the water safe to use again or to let out.
Application Area | Benefit Provided |
|---|---|
Dyeing Agent | Even color, improved dye uptake |
Binder/Additive | Stronger paper, better surface, improved coating |
Water Treatment | Removes heavy metals, keeps water clean |
Note: Clean water helps protect machines and makes sure the paper is safe and good quality.
Leather Dyeing
Color Enhancement
Leather dyeing needs careful work to get nice, even colors. Dispersants are very important for this. They help dyes spread out all over the leather. This stops spots and lines from showing up. These marks can make leather goods look bad. When factories use dispersants, the colors look brighter. The leather also gets a deeper and richer shade.
Dispersants help in leather work.
They make sure chemicals and dyes go on evenly.
Using dispersants makes colors brighter and stronger.
Even dye spreading gives better and more even results.
These things help leather look deeper and more colorful.
Things like shoes, bags, and couches made of leather get better with these changes. People want leather items to look the same and keep their color. Dispersants help keep the dye steady during the process. This gives leather a smooth look and colors that pop.
Tip: Even color makes leather look better and worth more.
Process Improvement
Leather dyeing has many steps. Each step must go well for good results. Dispersants help by keeping dye mixes steady. They stop dyes from sticking together or sinking in the dye bath. This helps dyes go deep into the leather.
Factories sometimes have problems like uneven color or slow dyeing. Dispersants fix these by helping dyes soak in faster. This means less time and fewer repeats. The work goes faster, and the leather meets high standards.
Here is a table that shows the main ways dispersants help:
Process Challenge | Dispersant Solution | Result |
|---|---|---|
Uneven dye uptake | Keeps dye spread out | Even color |
Dye clumping | Stops dyes from sticking | Smooth finish |
Slow dyeing | Helps dyes soak in | Quicker work |
Resource wastage | Cuts down on re-dyeing | Saves money |
Leather makers like these good points. They can make more products faster and with fewer mistakes. Dispersants help with both quality and speed, so they are very important in leather dyeing today.
Wood Stain

Color Uniformity
People who work with wood want stains that give even color. If the stain is not even, the wood can look patchy or messy. Sodium humate helps stains look the same everywhere on the wood. Its natural pigment lets the stain mix well and shows the wood’s grain. The color looks rich and earthy but does not hide the wood’s beauty.
Many people like a matte finish for a natural look. Stains with sodium humate give this effect and let you see the wood’s texture. The stain does not cover the grain. It makes the grain stand out more. This is good for things like furniture, floors, and panels where looks are important.
Note: Experts say to work in small sections. This stops the stain from drying too fast and helps blend it well.
The stain also helps protect the wood. It makes a layer that keeps out water, sunlight, mildew, and bugs. This layer helps the wood last longer and stay strong.
Feature | Benefit Provided |
|---|---|
Color Uniformity | Even, rich, and natural appearance |
Matte Finish | Highlights wood grain and texture |
Protective Properties | Guards against moisture and UV damage |
Penetration
It is important for stain to go deep into the wood. This helps the color last and keeps the wood strong. Sodium humate stains soak into the wood fibers, not just the top. This helps the color spread out evenly inside the wood.
Makers say sodium humate helps stains go deeper in many wood types. There is no exact data for each type, but the results are good. When the stain goes deep, the color stays bright even after use or sanding.
Deep penetration helps:
Color last a long time
Stop fading and surface damage
Keep the wood looking the same
These stains dry in a normal amount of time. Most jobs take a few hours or up to a day, depending on the wood and weather. Sodium humate does not make the stain dry faster or slower. It gives enough time to spread and fix the stain as needed.
Tip: Stains that go deep help wood look nice, even after years of use.
Advantages
Benefits Summary
Sodium humate gives many good things when used in paper, leather, and wood stain dyeing. Its special chemical structure brings important benefits. These help make products better and help factories work faster.
Enhanced Color Performance: Sodium humate helps dyes spread out well. This makes colors look brighter and more even in paper, leather, and wood.
Improved Material Strength: In paper, sodium humate acts like glue. It makes the final product stronger and harder to break.
Efficient Water Treatment: Sodium humate can take out heavy metals and bad stuff from water. This keeps the factory cleaner and safer.
Cost Savings: Factories use less dye and fewer chemicals with sodium humate. This helps save money on making things.
Eco-Friendly Profile: Sodium humate comes from nature. It is safe for people and breaks down in the environment.
Versatile Application: The compound works in many pH levels. It fits different factory jobs without losing its power.
Sodium humate is a helpful additive. It helps make good products and supports green ways of making things.
Here is a table that shows its main benefits:
Benefit Area | Impact on Industry |
|---|---|
Color Enhancement | Brighter, more even colors |
Strength Improvement | Stronger, longer-lasting materials |
Water Purification | Cleaner water, safer discharge |
Cost Efficiency | Lower chemical and dye usage |
Environmental Safety | Reduced pollution, safer for workers |
Considerations
Sodium humate has many good points, but factories should think about a few things before using it.
Source Variability: The quality of sodium humate can change. It depends on what it is made from. This can change how well it works in dyeing or as glue.
Process Compatibility: Not all factories work the same way. Sodium humate may need to be tested to see if it fits with the machines.
Color Influence: Sodium humate is dark. Sometimes it can change the color of light items a little bit.
Storage and Handling: Sodium humate soaks up water from the air. It should be kept in closed containers to stop it from clumping.
Regulatory Compliance: Some places have rules about what can be used in factories. Companies should check the rules before using a lot of sodium humate.
Tip: Always try sodium humate in small amounts first. This helps make sure it works well and stops surprises.
Factories that know these things can use sodium humate better. Good planning helps get the best results in paper, leather, and wood stain work.
Trends
Innovations
Scientists are finding new ways to use sodium humate in factories. One new idea is to mix sodium humate with magnetic nanoparticles like Fe3O4. They stick sodium humate onto these tiny magnets to make hybrid adsorbents. These new materials can grab dyes from water better than before. Magnets can pull them out, so they are easy to remove and use again. This helps get rid of dyes like malachite green and methylene blue. The process uses chemisorption and ion exchange, so dyes stick tightly to the material. Factories can use these hybrid adsorbents to clean dye-filled water. These materials stay strong and work well even after many uses.
Another new thing is composite hydrogels. These mix sodium humate with guar gum and special metal-organic frameworks called MIL-100(Fe). The in situ synthesis method helps everything blend and stay stable. The hydrogel can soak up lots of dyes and heavy metals. It uses hydrogen bonding and electrostatic attraction to trap bad stuff. This fixes problems with old materials that did not mix well or lost power fast. The new hydrogels help remove dyes better and are safer for the environment.
These new ideas show sodium humate can do more than help with color. It can also help clean up factory waste and make dyeing greener.
Future Uses
The future for sodium humate in dyeing looks good. Experts think new types of sodium humate will come soon. Some may be smart additives that change how they work as needed. For example, factories might use sodium humate that reacts to temperature or pH changes. This would help control how much dye sticks and how bright the color is.
Sodium humate could also help in closed-loop water systems. In these, factories clean and reuse water instead of throwing it away. Sodium humate can remove heavy metals and dyes, so it is great for this job. As more companies try to save water and stop pollution, more will want sodium humate.
Some scientists are testing sodium humate in digital printing and new coatings. These uses could make paper and leather with special features, like anti-bacterial surfaces or stronger materials. The need for eco-friendly products will push more research into natural additives like sodium humate.
Potential Future Use | Benefit Provided |
|---|---|
Smart dyeing additives | Better control of color and process |
Water recycling systems | Cleaner water, less waste |
Advanced coatings | New product features, safer materials |
Sodium humate is ready to help make the next generation of safe and high-quality materials for many industries.
Sodium humate is a strong helper in making paper, leather, and wood stains. It makes colors look better and helps materials last longer. It also helps factories keep things cleaner. Experts think more people will use sodium humate because it is good for the environment. But there are still some problems. Making sodium humate can cost a lot. Getting enough of it and following rules can be hard. Many companies want to use sodium humate because it works in many ways and is better for nature. In the future, new ideas might help use sodium humate in farming, cleaning water, and other jobs.
FAQ
What is sodium humate used for in paper manufacturing?
Sodium humate helps paper keep color even. It also makes paper stronger. It grabs heavy metals from water used in making paper.
Does sodium humate affect the color of finished products?
Sodium humate can make light items look a bit darker. Factories test small amounts first. This helps make sure the color is right.
Is sodium humate safe for workers and the environment?
Sodium humate is safe and breaks down in nature. It does not make bad fumes or waste. Factories use it to keep work and nature safe.
How does sodium humate improve leather dyeing?
Sodium humate helps dyes spread out on leather. It stops streaks and spots. This makes leather colors look deep and even.
Can sodium humate be used with all types of dyes?
Sodium humate works with many kinds of dyes. But, factories should test first. Some dyes may act differently.
What storage conditions does sodium humate require?
Sodium humate soaks up water from air. Factories keep it in closed boxes in dry places. This stops it from sticking together.
Does sodium humate help with water recycling in factories?
Yes. Sodium humate takes out metals and dye leftovers from water. This lets factories use water again and helps nature.
How does sodium humate affect wood stain performance?
Sodium humate helps stain go deep and look even. It gives wood a natural, flat look. It also helps protect wood from water and sun.
See Also
Understanding Humate Benefits And Its Importance In Agriculture
Comparing Humic Acid And Chemical Fertilizers For Sustainability
Top Plants That Thrive When Treated With Humic Acid
