Understanding Bio Fertilizers and Their Role in Modern Farming

Have you ever thought about how to grow more crops and help the environment? Bio fertilizers are a good way to do this in farming today. These products use living microorganisms to make soil better and help plants grow. More people around the world are using them because they want organic food and less chemical fertilizer. Studies show bio fertilizers can help wheat and maize grow up to 45% more. They also add more carbon and nitrogen to the soil. You can help make soil healthy, grow more crops, and protect the environment with these new products.
Key Takeaways
Bio fertilizers use living microbes to help plants grow. They also make soil better in a natural way. They help crops grow more by making nutrients easier to get. Plants can take in nitrogen and phosphorus more easily. Using bio fertilizers makes soil healthier and holds water better. This means farmers need less chemical fertilizer. There are different types like bacterial, fungal, and algal bio fertilizers. Each type helps plants in its own way. Bio fertilizers help the environment by lowering pollution. They also cut down on greenhouse gases and chemical runoff. You can use bio fertilizers in many ways for good results. You can treat seeds, mix them in soil, or spray them on leaves. Mixing bio fertilizers with compost or manure helps soil even more. It also makes crops stronger. Storing bio fertilizers the right way is important. Picking the best product for your soil and weather helps you get the most benefits.
Bio Fertilizers
Definition
Bio fertilizers are products that use living microorganisms to help crops grow better. These microorganisms, like bacteria, fungi, and algae, live in the soil or on plant roots. They make nutrients easier for plants to use and help keep soil healthy. Many countries and scientists have their own ways to define bio fertilizers. The table below shows how different groups describe them:
Source / Region | Definition Summary | Key Microbial Functions | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
India (Essential Commodities Act, 1985) | Product with living microorganisms that help farming by fixing nitrogen, making phosphorus available, or moving nutrients to boost soil and crop growth. | N fixation, P solubilization, nutrient mobilization | Legal definition; biofertilizers are on the important list. |
Brazil (Decree No. 8.384, 2014) | Product with an active part or organic agent, with no pesticides, that helps plants grow more, no matter if it has hormones or not. | General microbial activity on plants | Broader legal meaning; separates inoculants as products with microorganisms. |
European Union (Regulation 2019/1009) | Microbial biostimulants are products that help plants use nutrients better, handle stress, and improve quality or nutrient use. | Microbial biostimulants helping nutrient use and plant growth | Biofertilizers are a type of biostimulant; there are rules for quality and safety. |
Scientific literature (Vessey, 2003) | Substance with living microorganisms that live near roots or inside plants and help them grow by giving more nutrients. | Colonization, nutrient supply enhancement | Focuses on how microbes and plants work together. |
Scientific literature (Dineshkumar et al., 2018) | Products (solid or liquid) with living or sleeping microbes (bacteria, fungi, actinomycetes, algae) that fix nitrogen from the air, break down soil nutrients, and make growth substances. | N fixation, nutrient solubilization, growth promotion | Shows that many kinds of microbes and actions are involved. |
Scientific literature (Kumar et al., 2022) | Mixes of living or sleeping microbial cells that help plants take up nutrients and grow better; groups include N-fixing, P/K solubilizing, zinc solubilizing, sulfur-oxidizing microbes, and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. | Many nutrient moving and growth helping jobs | Puts biofertilizers into groups by what the microbes do. |
Scientific literature (Shahwar et al., 2023) | Many products with living or sleeping microorganisms that help crops grow and give more yield. | Growth and yield improvement | This is a wide and open meaning. |
Scientific literature (Malusá and Vassilev, 2014) | Product ready to sell with microorganisms that go on plants or soil to help them grow by making more nutrients available; not the same as organic or mineral fertilizers or biostimulants with dead cells or extracts. | Microbial inoculants helping nutrient availability | Explains how the product is made and ready to use. |
All these definitions show that bio fertilizers use living microbes to help plants grow and make soil better. Chemical fertilizers add nutrients right away, but bio fertilizers help plants get more from the soil by making nutrients easier to take in.
Key Features
When you use bio fertilizers, you get some important benefits:
Living Microorganisms: These products have bacteria, fungi, or algae that stay alive until you put them on your crops.
Natural Nutrient Cycling: The microbes help move nutrients around in the soil so plants can use them.
Eco-Friendly: Bio fertilizers do not harm the environment. They help you use less chemical fertilizer, which can hurt soil and water.
Soil Health Improvement: Using these products can make soil structure and fertility better over time.
Targeted Action: Different bio fertilizers work in special ways, like fixing nitrogen or making phosphorus easier to use.
Tip: You can use bio fertilizers with organic farming to get even better results for your crops and the environment.
How They Work
Bio fertilizers help your plants grow stronger and healthier by using natural processes. Here are the main ways they help:
Nitrogen Fixation
Some bacteria in bio fertilizers, like Rhizobia, can take nitrogen from the air and change it into a form plants can use. You will not need as much chemical nitrogen fertilizer when you use these products. The bacteria live in the soil or on roots and give plants a steady supply of nitrogen.
Phosphate Solubilization
Many soils have phosphorus, but plants cannot always use it. Some microbes in bio fertilizers break down phosphorus compounds and release them into the soil. Plants can then take in this important nutrient more easily. This helps you get better growth without adding extra phosphate fertilizers.
Growth Promotion
Bio fertilizers also help plants grow by making natural substances called phytohormones. These hormones help roots grow and let plants take in more nutrients. Some microbes even protect crops from bad diseases by making antibiotics or enzymes that fight off harmful germs.
Microbes in bio fertilizers can:
Fix nitrogen from the air for plants.
Break down and move phosphorus.
Make growth substances like phytohormones.
Stop plant diseases by making antibiotics and enzymes.
Make soil structure and fertility better.
Bio fertilizers work in a different way than chemical fertilizers. Chemical fertilizers give nutrients right away, but they can hurt the environment if used too much. Bio fertilizers use natural ways to make nutrients available and keep soil healthy. This helps you grow strong crops and protect the land for the future.
Types

Bio fertilizers come in different types. Each type helps your crops and soil in special ways. You can pick from bacterial, fungal, or algal bio fertilizers. These products use nature to make soil better and help plants grow. Many farmers also use natural fertilizers from plants or animals. These include compost, manure, and kelp meal. They help soil organisms and make crops grow more.
Plant-based biofertilizers: alfalfa meal, cottonseed meal, liquid kelp, kelp meal, compost, compost tea, molasses, cover crops
Animal-based biofertilizers: manure, manure tea, bone meal, blood meal, urea, fish emulsion, milk
These natural fertilizers give important nutrients. They also help good soil organisms live and grow.
Bacterial
Bacterial bio fertilizers use living bacteria to help plants. These bacteria live in the soil or on roots. They fix nitrogen and make phosphorus and potassium easier for plants to use. Many products have different kinds of bacteria. The Bacillus group is the most common. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, Bacillus subtilis, and Bacillus licheniformis are used a lot. These bacteria help plants grow, add nutrients to soil, and fight diseases.
Bacterial Species / Genus | Specific Functions in Biofertilizers |
|---|---|
Azotobacter, Rhizobium, Frankia, Azospirillum spp., Herbaspirillum spp., Alcaligenes, Enterobacter, Azoarcus spp., Acetobacter diazotrophicus | Nitrogen fixation - converting atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into plant-available forms |
Bacillus edaphicus, Arthrobacter spp., Bacillus, Bacillus circulans | Potassium solubilization - producing organic acids to solubilize potassium ions |
Pseudomonas striata, Bacillus circulans, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus polymyxa, Agrobacterium, Micrococcus, Flavobacterium | Phosphorus solubilization - dissolving bound phosphates by secreting organic acids and lowering soil pH |
Thiobacillus spp. | Sulfur oxidation - converting sulfur to sulfate, a usable form for plants |
Pseudomonas spp., Mycorrhiza, Bacillus spp. | Zinc solubilization - making zinc available to plants |
These bacteria help with different nutrient cycles. Bacillus subtilis makes growth substances and helps fight plant diseases. Rhizobium and Azospirillum fix nitrogen so crops get more of it.
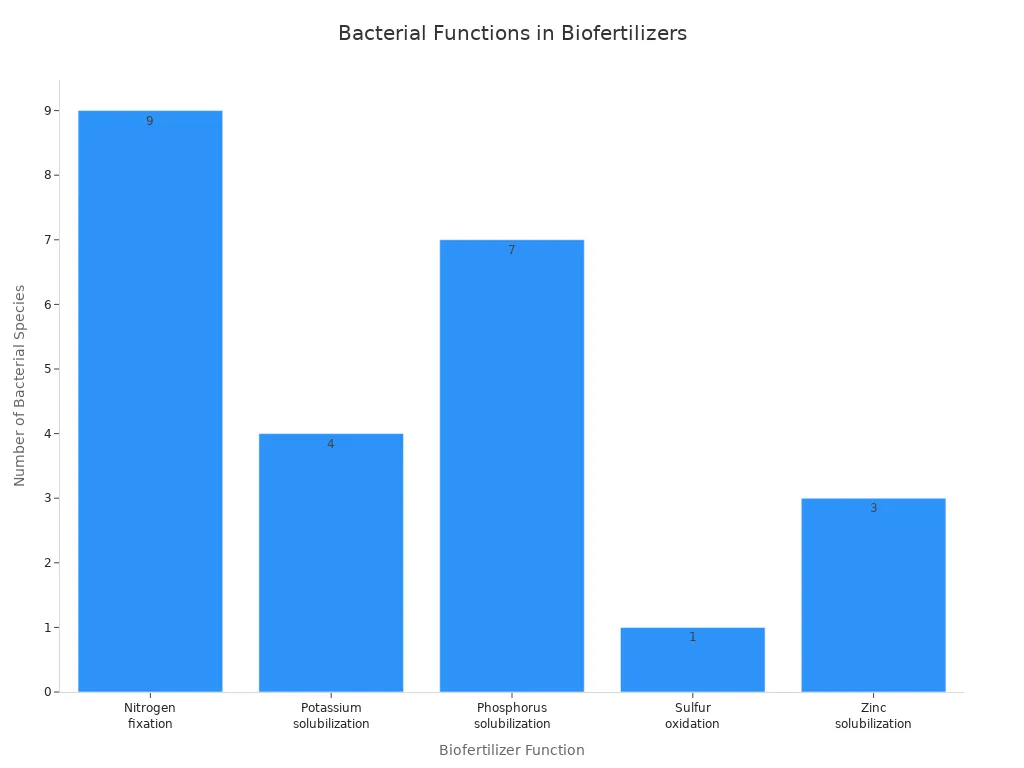
Note: Microbial inoculants like these bacteria help plants get more nutrients and grow stronger.
Fungal
Fungal bio fertilizers use good fungi to help plants and soil. The most important group is arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF). These fungi join with plant roots. They make roots bigger and help plants take in more nutrients. AMF help plants get more phosphorus, nitrogen, and other nutrients. They also make soil better by sticking soil pieces together. This makes soil stronger and helps plants during drought, cold, or when there are heavy metals.
When you use fungal bio fertilizers, your crops can grow bigger and stronger. AMF also help soil by supporting good microbes and lowering the need for chemical fertilizers. You can keep AMF high by using less tillage and fewer chemicals.
Tip: Fungal bio fertilizers help plants survive hard times and give better yields in a natural way.
Algal
Algal bio fertilizers use algae and cyanobacteria to help soil and plants. Cyanobacteria like Anabaena, Nostoc, and Oscillatoria fix nitrogen from the air. This adds nitrogen to the soil. Green microalgae such as Chlorella and Spirulina help crops grow and add nutrients to soil. Seaweed like Sargassum and Gracilaria add organic matter, balance soil pH, and lower the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio.
Cyanobacteria fix nitrogen from the air for crops.
Microalgae add phosphorus, nitrogen, and organic carbon to soil.
Algal bio fertilizers help good soil microbes and control plant diseases.
Seaweed and microalgae make soil better, lower salt, and balance pH.
You can use algal bio fertilizers to avoid heavy metal pollution. They help you farm in a clean and safe way. These products help you grow healthy crops and protect the earth.
Callout: Algal bio fertilizers are a green way to make soil better and grow more crops. They are a smart choice for farming today.
Benefits
Soil Health
Bio fertilizers can make your soil healthier. They add living microorganisms to the soil. These microorganisms help create a strong place for your crops. Over time, your soil will have more organic matter and nutrients. Using bio-organic fertilizers for many years makes soil quality better. It also helps the soil do more jobs, like breaking down nutrients. You will see more enzyme activity and better nutrient cycling. The soil will have more types of helpful microbes. These changes make soil stronger and help it grow more crops.
Bio fertilizers also help soil fight problems like acidification. For example, banana farmers who used bio-organic fertilizers saw big changes. Their soil had almost twice as much organic matter and nitrogen. The soil could also stop acids from causing damage. You will find more good bacteria, like Bacillus, in your soil. These bacteria help plants grow well. Chemical fertilizers can cause more bad bacteria and hurt the soil. By using bio fertilizers, you make soil healthier and better for farming.
Tip: Healthy soil gives you stronger crops and means you need fewer chemicals later.
Nutrient Availability
Bio fertilizers help crops get nutrients in a natural way. The microorganisms break down organic matter slowly. This slow process gives plants nutrients when they need them. It also stops too much fertilizer from hurting plants. Synthetic fertilizers release nutrients fast and can cause problems. Bio fertilizers give a steady supply of nutrients. This helps plants grow without hurting the soil or the environment.
Feature | Bio (Organic) Fertilizers | Synthetic Fertilizers |
|---|---|---|
Nutrient Source | Derived from natural materials; nutrients released gradually through microbial activity | Chemically manufactured; nutrients are rapidly available |
Nutrient Release Rate | Slow and steady, optimal for plant uptake, reducing overfertilization risks | Fast release, can cause nutrient leaching or root burn |
Soil Health Impact | Improves soil structure, fertility, and microbial activity; adds organic matter | Can degrade soil microbiology and chemical structure over time |
Environmental Safety | Minimal risk of pollution; no toxic buildup in soil | Higher risk of environmental pollution and greenhouse gas emissions |
Nutrient Completeness | Provides meso- and micronutrients often missing in synthetics | Primarily supplies NPK; may lack micronutrients |
Dependence on Microbes | Requires active soil microbes for nutrient mineralization | Nutrients are directly available without microbial mediation |
Application Consistency | Nutrient content varies, making precise application difficult | Nutrient content is consistent and easily measured |
Water Retention | Enhances soil water-holding capacity through improved structure | Does not improve water retention |
Bio fertilizers also help soil hold more water. This supports plant roots and helps crops grow. Over time, you may not need to use as much fertilizer. This saves you money and work. The slow nutrient release means plants get what they need at the right time. This leads to healthier plants and bigger harvests.
Yield Improvement
Bio fertilizers can help you grow more crops. Many tests show that these products help plants get bigger and give more food. For example, using Rhizobium and phosphate solubilizing bacteria on faba beans helps a lot. You will see more grain, better nutrient use, and stronger plants. These good results happen with other crops too, like soybean and mung bean.
Rhizobium bacteria help plants make more pods and seeds. They do this by helping plants take in more nutrients, especially phosphorus.
Phosphate solubilizing bacteria make phosphorus easier for plants to use. This helps roots grow and flowers form.
Using different kinds of bio fertilizers together works even better. Plants take in more nitrogen, phosphorus, and micronutrients. This gives you higher yields.
You will see taller plants and more plant material. Plants will use soil nutrients better.
These changes mean you can use less chemical fertilizer and still get healthy crops.
Using bio fertilizers helps you farm in a way that is good for the earth and gives you better crops each year.
Environmental Impact
When you pick bio fertilizers, you help nature in many ways. These products make farming safer for the earth. You can notice changes in your fields, water, and air.
Using bio fertilizers means less greenhouse gas goes into the air. Chemical fertilizers, like ones that make ammonia, send out lots of carbon dioxide. Making ammonia alone causes up to 2% of the world’s CO2. Bio fertilizers can lower these gases by up to 78% for nitrogen and 41% for phosphorus when compared to mineral fertilizers.
Bio fertilizers help keep water clean. Chemical fertilizers often wash away and cause runoff. This runoff pollutes water, makes algae grow too much, and creates dead zones in lakes and rivers. Bio fertilizers give out nutrients slowly, so plants use them better and less washes away.
They keep soil healthy. Bio fertilizers add helpful microbes to the ground. These microbes fix nitrogen, make nutrients easy for plants, and help soil stay rich. Chemical fertilizers can hurt these good microbes and cause heavy metals to build up in the soil.
Bio fertilizers help with natural pest control. Some have bacteria that keep bad bugs away. These bacteria do not harm bees or other good insects. You can use fewer chemical sprays, which helps all living things.
They help plants fight sickness. Bio fertilizers bring in microbes that stop bacteria and fungi. These microbes control plant diseases and nematodes without hurting soil or water.
Your crops get stronger. Drought-resistant bacteria and fungi in bio fertilizers help plants live when it is dry. Your crops can grow well even if there is not much water.
Bio fertilizers help farms last longer. Using them protects the land for the future. You stop soil from washing away, keep nutrients in the ground, and support organic farming.
🌱 Tip: Every time you use bio fertilizers, you help make air cleaner, water safer, and soil healthier. Your choices help the planet.
Applications

Usage Methods
There are many ways to use biofertilizers on your farm. Each way works best for certain crops or systems. Here are some common ways to use them:
Seed Treatment: You can cover seeds with a biofertilizer mix before planting. This helps good microbes stick to the seeds and help them grow.
Seedling Root Dip: Dip young plant roots in a biofertilizer liquid before moving them to the field. This is good for rice, vegetables, and fruit plants.
Direct Soil Application: Mix biofertilizer with compost or manure and spread it on the field. This helps the soil and works for many crops.
Tuber Inoculation: Put biofertilizer on tubers like potatoes before planting. This helps roots grow and take in more nutrients.
Foliar Spray: Spray a weak biofertilizer mix on plant leaves. Plants can quickly take in nutrients this way and recover from stress.
Liquid Application: Use liquid biofertilizer for seeds, roots, or soil. Liquid types are easy to use and spread well.
Tip: Pick the method that fits your crop and local area for the best results.
Crop Suitability
Biofertilizers work for many crops, but some do even better. Barley grows stronger and gives more grain, even in salty dirt. Vegetables and legumes like beans and peas often give the biggest harvests. These crops get more nutrients and have better roots.
Tests show that using biofertilizers with less mineral fertilizer still gives good results. This works for big crops like maize, wheat, and rice. You will see better growth, more nutrients used, and healthier soil in many types of farms.
🌱 Note: Vegetable, legume, and cereal crops do very well with biofertilizer. They are a smart pick for all kinds of farms.
Integration with Other Inputs
You can use biofertilizers with other farm products to get better results. Many farmers mix biofertilizers with compost, biochar, or animal manure. This mix makes soil stronger, holds water better, and gives more nutrients. For example, adding biochar with Bacillus subtilis helps crops grow bigger and better.
Biofertilizers work well with less chemical fertilizer. This means you use fewer chemicals and save money.
Using biofertilizers with compost or manure helps good soil microbes and makes plants stronger against disease and stress.
These ways add more organic matter, potassium, and phosphorus to the soil. They also help crops grow during dry or hard times.
You may need fewer chemical sprays because some biofertilizer microbes protect plants from pests and sickness.
Callout: Mixing biofertilizers with other inputs makes a balanced system. You get healthy crops, spend less, and help the earth.
Big farms have already had good results with these mixes. In Brazil, farmers use biofertilizers with other products instead of synthetic nitrogen. This has made crops better, helped new farm businesses, and led other countries to try the same thing.
Comparison
Chemical vs. Bio Fertilizers
You have to pick how to feed your crops. Chemical fertilizers and bio-based fertilizers work in different ways. Chemical fertilizers give plants nutrients very fast. This makes plants grow quickly. But this fast growth can cause problems. Using chemical fertilizers for a long time can hurt the soil. They can lower the number of good microbes in the soil. The soil may lose its natural balance. You might see the soil get hard or not hold water well.
Bio-based fertilizers work slower. They release nutrients over time. These fertilizers help good microbes in the soil. They make the soil structure better and keep the pH balanced. This helps your crops grow strong. You also help the environment when you use these products.
Aspect | Chemical Fertilizers | Biofertilizers / Bio-organic Fertilizers |
|---|---|---|
Nutrient Release | Fast-acting, immediate nutrient availability | Slow and steady nutrient release, mimics natural uptake |
Soil Microbial Impact | Can reduce microbial diversity and harm soil microbes | Increases microbial diversity and biomass, improves soil health |
Soil Structure | Can degrade soil structure over time | Enhances soil physical and chemical properties |
Soil Fertility | May cause nutrient imbalance and soil degradation | Contributes to sustainable soil fertility |
Crop Yield Impact | High initial yield but may cause nutrient deficiencies | Can maintain or increase yield while reducing chemical use |
Environmental Impact | Risk of runoff, pollution, and soil pollution | Environmentally friendly, reduces chemical fertilizer load |
Long-term Sustainability | Relies on non-renewable resources, may degrade soil | Renewable, promotes sustainable agriculture |
🌱 Note: If you choose bio-based fertilizers, you help your crops and protect your land for the future.
Cost and Sustainability
You want your farm to do well every year. Cost and sustainability are important for your choice. Chemical fertilizers might look cheaper at first. They give fast results, but you may pay more later. Using too much can damage soil and water. Fixing these problems costs more money.
Bio-based fertilizers can help you spend less per acre. For example, you might pay $48 per acre for chemical fertilizers. With bio-based fertilizers, you may only pay $25.80 per acre. If you use both together, you can get up to 46% more crops. Your soil will hold water better and your plants will be healthier. These good changes last for many years.
You lower the chance of nutrient runoff and pollution.
You help more good microbes live in the soil.
Your crops can fight drought and disease better.
You make less greenhouse gas and keep water clean.
💡 Tip: To farm in a sustainable way, use the right product at the right time. Watch your soil’s health. This helps you save money and care for the earth.
Challenges
Effectiveness Factors
Bio fertilizers do not always work the same everywhere. Many things can change how well they help crops. Soil pH is very important. Some fertilizers work best in soils with a pH of 8.0. The size of the fertilizer pieces matters too. Small pieces spread better and reach roots faster.
Weather also affects how nutrients get to plants. Temperature, humidity, and soil microbes all play a part. Controlled-release fertilizers change how fast they give out nutrients. This helps plants get what they need at the right time. Some additives, like phosphate boosters or biostimulating compounds, help plants use more phosphorus. Biochar-based fertilizers and solubilizing bacteria also help plants take in more nutrients.
Tip: Test your soil and pick the right bio fertilizer for your area. This helps you get the most from your money.
Storage and Handling
You need to store and handle bio fertilizers carefully. This keeps the microbes alive and working. The number of living microorganisms in each product is important. If you do not store them right, you can lose these helpful microbes before using them.
Here are some tips for storage and handling:
Keep bio fertilizers in a cool place below 35°C.
Store them dry and away from water to stop clumping.
Use airtight containers if the package is broken.
Keep all products out of direct sunlight.
Label packages with batch numbers, expiry dates, and instructions.
Store bio fertilizers away from chemicals and synthetic fertilizers.
Use older stock first and check for damage or spoilage.
🧪 Note: Good storage and handling keep your bio fertilizers safe and useful for your crops.
Adoption Barriers
There are some problems when you try to use bio fertilizers on your farm. Some problems come from the products. Others are about your money, tools, or what you know.
Barrier | Description and Impact on Adoption |
|---|---|
Labor Requirements | Using bio fertilizers takes time and work. If you do not have enough help or tools, it can be hard. |
Bulkiness and Transport | These products can be heavy and hard to move. This is worse if your farm is far away or roads are bad. |
Availability and Access | Sometimes, bio fertilizers are hard to find or not always in stores. This makes it tough to use them often. |
Technical Know-How | You need to know the right type, amount, and time to use them. Without good advice, you may not get the best results. |
High Costs and Low Income | If you do not make much money, buying bio fertilizers can feel risky. More money makes it easier to try new things. |
Limited Access to Credit | Without loans or credit, you may not have enough money to buy what you need. |
Trust and Knowledge | Trust and knowing about bio fertilizers are important. If you do not get support or information, you may not want to try them. |
Many farmers want more help from experts and farmer groups. You may feel unsure about new products if you do not see good results or get enough information. Field demonstrations and expert advice can help you trust and learn how to use bio fertilizers.
🌱 Callout: Trust and learning are just as important as the products. Ask for help and look for local demos to learn more.
Future Trends
Innovations
New technology is changing how you use bio fertilizers. Scientists now use nanotechnology to make bionanofertilizers. These products have a special nanoencapsulation coating made of tiny polymers. This coating protects the microbes and helps them live longer. It also lets nutrients come out slowly over time. This means the products last longer and work better in your fields.
Nanoparticles such as silica, zinc oxide, and iron nano-oxide help move nutrients to plants. These particles make enzymes work better and help good microbes grow in the soil. Your crops get stronger and can fight off diseases more easily. Bionanofertilizers fix old problems like short shelf life and being hurt by weather.
There are also smart fertilizers that give nutrients only when plants need them. Some use silica nanoparticles that react to signals from plant roots. Others, like "Smart-N," release nutrients when roots send out special chemicals. These new products help you use less fertilizer and waste less.
Other new ideas include:
Microbial inoculants with many helpful soil species to make plants healthier.
Biostimulants from seaweed extracts that help plants take in more nutrients.
Eutectic mixture technologies that help fertilizers last longer and stop nitrate loss.
Liposome carriers that bring nutrients right to the roots.
Synthetic plant growth hormone derivatives that help plants grow longer and lose fewer nutrients.
💡 Tip: These new ideas help you use fertilizers better, protect nature, and grow healthier crops.
Market and Policy
The biofertilizer market is growing very fast. More people want organic food and farming that is good for the earth. Governments help by giving money, tax breaks, and research support for bio-based fertilizers. These rules make it easier for you to use eco-friendly products and use fewer chemicals.
Many countries now limit chemical fertilizers to keep soil and water safe. You can farm more safely with biofertilizers because they do not pollute. People also want food without chemicals, so the market keeps growing. In North America, strong rules and new farming ways make this area a leader in using biofertilizers. Asia-Pacific and Africa are growing fast because they have many people and need to protect the environment.
Here is a table showing how the global market will grow:
You can see the biofertilizer market will almost double by 2030 and triple by 2034. This growth is much faster than the regular fertilizer market, which grows only 4.1% each year.
🌱 Note: As more farmers learn about biofertilizer benefits and as governments help, it will be easier for you to use these products and help farming stay healthy for the future.
You can make farming better by picking eco-friendly choices. Bio-based products make soil healthier, help crops grow, and save money.
They cut down on pollution and help crops stay strong.
To begin, plant cover crops, use fewer chemicals, and join local classes. Talk with experts and other farmers to learn new ways.🌱 Start now—help farming be sustainable for a healthier earth and bigger harvests.
FAQ
What are bio fertilizers made of?
Bio fertilizers have living microorganisms like bacteria, fungi, or algae. These microbes help plants get nutrients from soil. You can buy them as powder, liquid, or granules.
Can you use bio fertilizers with chemical fertilizers?
Yes, you can use both at the same time. Bio fertilizers make soil healthier and help plants use nutrients. You might need less chemical fertilizer if you add bio fertilizers.
How do you store bio fertilizers?
Keep bio fertilizers in a cool and dry place. Do not let sunlight or water touch them. Always look at the expiration date before using. Good storage keeps the microbes alive.
Are bio fertilizers safe for the environment?
Bio fertilizers do not pollute soil or water. They help keep soil healthy and stop bad runoff. Using them helps protect the environment.
Which crops benefit most from bio fertilizers?
Legumes, cereals, and vegetables grow well with bio fertilizers. You can use them on rice, wheat, beans, maize, and many garden vegetables. Most crops grow better and give more food.
How long does it take to see results from bio fertilizers?
You may see healthier plants and soil in a few weeks. Full results often show after one or two growing seasons. Using them often gives the best results.
Do bio fertilizers replace compost or manure?
Bio fertilizers work best when used with compost or manure. You get stronger soil and healthier plants by mixing them. Each one gives your farm different benefits.
💡 Tip: Always read and follow the label instructions to get the best results from bio fertilizers.
See Also
How Humic Acid Fertilizers Manage Nutrients For Sustainable Farming
Key Differences Between Biochemical And Mineral Fulvic Acids Explained
Comparing Humic Acid And Chemical Fertilizers For Eco-Friendly Farming
How Organic Fertilizers Support Healthy Plants And Soil Naturally
