What Is Ammonium Humate and How Does It Work in Soil

Ammonium humate is an organic fertilizer and soil conditioner. It helps make soil better and helps plants grow. This humate type makes nutrients easier for plants to use. It also helps roots grow strong. Scientists found that humate use raises chlorophyll in plants. It also helps plants take in more nutrients, even when water is low. Using ammonium humate makes crops grow much better. The table below shows these big improvements:
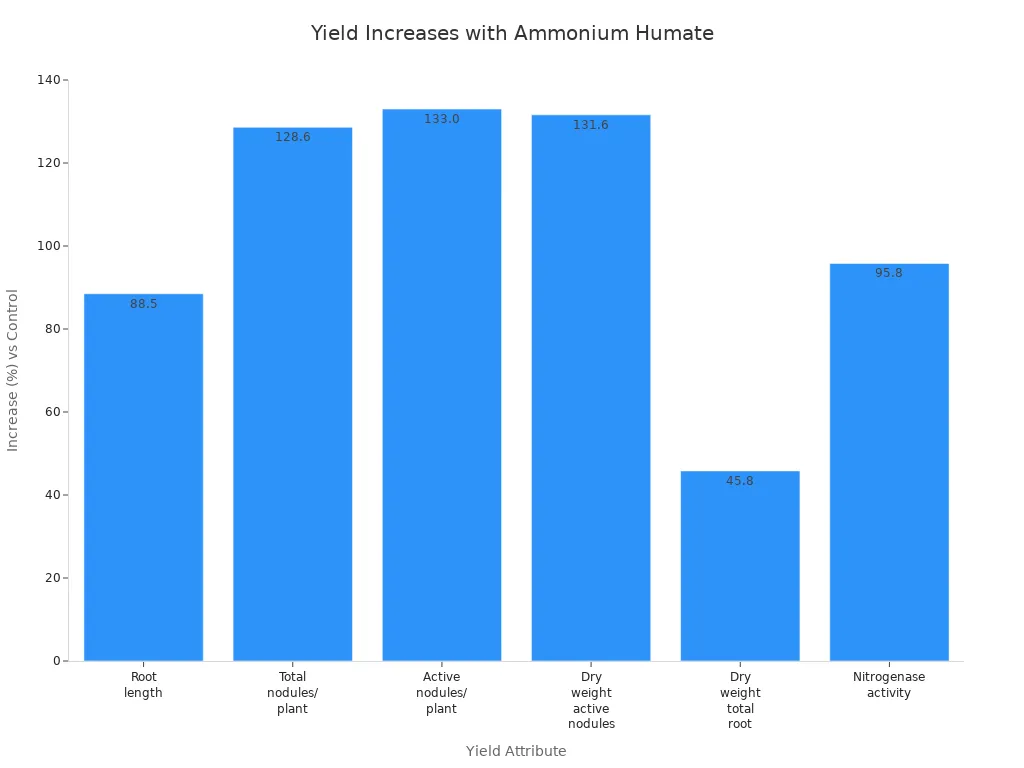
Parameter | Treatment vs Untreated Control | Increase (%) |
|---|---|---|
Root length | RA3 vs RA0 | +88.5 |
Total number of nodules/plant | RA3 vs RA0 | +128.6 |
Number of active nodules/plant | RA3 vs RA0 | +133.0 |
Dry weight of active nodules | RA3 vs RA0 | +131.6 |
Dry weight of total root | RA3 vs RA0 | +45.8 |
Nitrogenase activity | RA3 vs RA0 | +95.8 |
Learning about ammonium humate helps farmers get better soil. It also helps them grow more crops. This humate helps soil stay strong and helps plants grow well. It also helps farms make more food.
Key Takeaways
Ammonium humate is an organic fertilizer. It makes soil healthier and helps plants grow strong. It helps plants get nutrients more easily.
It mixes humic acids with ammonium. This gives soil both organic matter and nitrogen. These help roots grow better and keep nutrients in the soil.
Ammonium humate helps soil particles stick together. This makes soil hold water better and lets air move through. Roots become healthier this way.
It helps plants take in more nutrients. It turns on enzymes that help plants use nitrogen and other minerals well.
Using ammonium humate gives bigger crop yields. It also makes crops taste better and last longer.
This fertilizer works in many soil types. It helps sandy, clay, saline, and alkaline soils. It helps plants deal with stress like drought and salt.
The best way is to put ammonium humate right on the soil. The amount you use depends on the crop and soil.
Ammonium humate is good for the environment. It breaks down naturally and does not hurt soil or water. It helps farmers use better farming methods.
Ammonium Humate Overview
What Is Ammonium Humate
Ammonium humate is part of the humate fertilizer group. Scientists say it is an ionic salt. It forms when ammonium cations join with oxygen groups in humic substances. These groups are carboxylic, phenolic, and hydroxyl. Humic substances come from old plants and animals in soil. They make up complex and mixed molecules. Ammonium humate is special because it mixes ammonium with humic acids. This helps plants get nutrients more easily. It also helps soil keep nutrients and helps roots grow strong. Ammonium humate has both oxygen and nitrogen groups. This lets it hold onto metals and make complexes. These complexes can help soil grow better plants. But the bonds between ammonium and humic acids are not very strong. So, ammonium can still wash away from soil sometimes.
How It’s Made
People make ammonium humate by mixing humic acid with ammonium compounds. They start with materials that have lots of humic substances. These include leonardite, lignite, and peat. The table below shows the main sources:
Raw Material | Description | Geographic Sources | Humic Acid Content | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Leonardite | Main source for making ammonium humate | North Dakota (USA), Saskatchewan (Canada), China | 60–80% | Has more humic acid; export rules and environment laws apply |
Lignite | Another important source | Russia, Indonesia, Australia, China | Not specified | Export bans and environment checks affect supply |
Peat | Organic source of humic acids | Finland, Ireland, other peat-rich places | 25–40% | Rules protect nature and limit use; less humic acid |
Workers take humic acids from these materials. Then, they mix them with ammonium hydroxide or other ammonium salts. This makes ammonium humate, which has both humic acids and ammonium. The process also adds nitrogen and makes nitrogen fertilizer. The final product has lots of humic and ammonium parts. This mix helps soil and gives plants what they need.
Comparison to Other Humates
Ammonium humate is not the same as potassium humate or sodium humate. The big difference is the cation used to make them. Ammonium humate uses ammonium. Potassium humate uses potassium. Sodium humate uses sodium. To make ammonium humate, people mix humic acid with ammonium compounds. This also adds nitrogen fertilizer. Potassium and sodium humate are made to add salts and help soil, but they do not add nitrogen. Ammonium humate gives both humic substances and nitrogen. This is good for soil that needs both. Potassium and sodium humate give humic substances and their cations, but no nitrogen. Farmers pick the right humate for their soil, crops, and nutrients.
Tip: Ammonium humate helps soil by adding organic matter and nitrogen. This makes it useful for many kinds of soil.
Ammonium Humate Properties
Chemical Composition
Ammonium humate has a special mix of chemicals. This mix makes it different from other things added to soil. It has organic matter, humic substances, and important nutrients. The humic acids and ammonium ions work together. They help soil and plants get better. These parts make soil healthier and help plants grow.
Key Elements
Ammonium humate has carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and a little sulfur. These elements build the humic molecules. Ammonium ions add nitrogen, which plants need to grow. The mix of organic matter and nitrogen is important. This gives ammonium humate its special chemical features. Humic acids help hold nutrients in the soil. This makes it easier for plants to use them. These acids also help keep soil strong and healthy.
Trace Nutrients
Ammonium humate also has small amounts of other nutrients. These are called trace nutrients. They help plants stay healthy. The nutrients come from the original organic matter and from salts added when making ammonium humate. The table below lists these trace nutrients and how much is in the humate solution:
Trace Nutrient | Concentration in Humate Solution | Notes on Biological Activity |
|---|---|---|
Cobalt (Co) | Maximal biological activity; promotes increase in seedling roots | |
Manganese (Mn) | 0.001% | Maximal biological activity; promotes formation of lateral roots |
Copper (Cu) | Present (exact concentration not specified) | Included in humate preparations |
Zinc (Zn) | Present (exact concentration not specified) | Included in humate preparations |
Molybdenum (Mo) | Present as ammonium molybdate salt | Source of molybdenum in humate preparations |
Boron (B) | Present (exact concentration not specified) | Included in humate preparations |
Cobalt and manganese work best at 0.001%. If there is too much, they do not help as much. Other nutrients like copper, zinc, molybdenum, and boron also help plants grow. All these nutrients, with the main elements, make ammonium humate good for soil.
Structure
Ammonium humate has a complex and changing structure. Scientists say it is made of many small molecules mixed together. These molecules stick together in groups. The humic acids have many acidic groups, like carboxyl and phenolic groups. These groups join with ammonium ions. This changes the size and shape of the humic molecules.
The ammonium counterion holds more water than sodium. This changes the size and shape of humate molecules.
The supramolecular structure lets humic substances stick together in soil.
These features help ammonium humate hold nutrients and make soil better.
The way acidic groups and ammonium ions join helps keep the humate stable in different soils.
This special structure helps ammonium humate work well in soil.
Solubility and Stability
Ammonium humate dissolves well in water, especially if the pH is above 2. This makes it easy to use as a liquid. Plants can get its nutrients quickly. The table below shows how well different humic substances dissolve:
Substance | Solubility in Water | pH Condition |
|---|---|---|
Fulvic acid | Soluble | At any pH |
Humic acid | Soluble | At pH > 2 |
Humin | Insoluble | At any pH |
Because ammonium humate has humic acid, it dissolves in most soils. Its structure and ammonium ions help it stay stable. This means it does not break down fast. The nutrients and organic matter stay in the soil for a long time. This helps plants and keeps soil healthy.
Note: Ammonium humate is easy to use and lasts a long time. This makes it a good choice for farmers who want better soil and crops.
Sorption and Reactivity
Ammonium humate has special ways it acts in soil. These ways come from its humic structure and chemicals. Scientists look at how humic substances work in soil. They want to know why they help plants. Ammonium humate is different because it can hold nutrients and react with many things in soil.
Sorption Properties of Ammonium Humate
Sorption means a substance can grab and keep other molecules. Ammonium humate is good at this because of its humic acids. These acids have groups like carboxyl and phenolic. These groups can stick to metals, nutrients, and water. This helps plants get the nutrients they need.
Humic molecules in ammonium humate can trap heavy metals. This lowers the chance of metal problems in soil.
Its chemical structure lets it hold water. This keeps soil wet and helps plants grow.
Ammonium humate can grab nutrients like potassium, calcium, and magnesium. This stops these nutrients from washing away.
The table below shows how ammonium humate works with soil nutrients:
Nutrient | Sorption Strength | Effect on Soil Properties |
|---|---|---|
Potassium | High | Improves nutrient retention |
Calcium | Moderate | Supports soil structure |
Magnesium | Moderate | Enhances plant uptake |
Iron | High | Reduces deficiency risk |
Zinc | High | Increases bioavailability |
Reactivity in Soil
Reactivity means how something changes or reacts with other chemicals. Ammonium humate is very reactive because of its humic acids and ammonium ions. These parts can join with metals and nutrients. This changes the soil and helps plants get more food.
Humic acids in ammonium humate can react with iron and zinc. This makes these nutrients easier for plants to use.
The bonds in humic substances can break and join again. This helps ammonium humate work in many soils.
Ammonium ions in the humic structure can swap with other cations in soil. This helps keep soil chemistry balanced.
Note: Ammonium humate can help soils with too much salt or high pH. Its humic parts can balance pH and lower harm from extra salts.
How Sorption and Reactivity Improve Soil
The sorption and reactivity of ammonium humate help soil in many ways:
They help soil keep nutrients and water.
They stop important minerals from being lost.
They make the soil better for plant roots.
They help soil by grabbing harmful metals.
They make fertilizers work better by making nutrients easier to use.
These features make ammonium humate great for soil health. Farmers and gardeners use it to help crops grow and protect soil.
Summary Table: Key Sorption and Reactivity Properties
Property Type | Description | Benefit to Soil |
|---|---|---|
Sorption | Binds nutrients, water, and metals | Reduces nutrient loss |
Reactivity | Forms complexes with soil chemicals | Increases nutrient use |
Cation Exchange | Swaps ammonium with other soil cations | Balances soil chemistry |
Buffering | Stabilizes soil pH and chemical properties | Protects plant roots |
Ammonium humate uses its humic structure and chemicals to help soil. Its power to grab and react with many things makes it a strong soil helper. These actions keep soil healthy and help plants grow strong.
Soil Properties and Improvement
Physical Effects on Soil
Ammonium humate changes how soil acts in many ways. Its humic content helps soil keep more water. It also makes the soil structure better. Scientists saw these effects, especially with ammonium humate in a hydrogel. Some main improvements are:
A hydrogel with humic acid and quaternary ammonium guar gum made soil hold twice as much water.
Soil particles stuck together 650% more. This means soil holds together better and is less loose.
These changes make soil have more spaces for air and water. Roots can grow deeper.
The hydrogel lets out humic acid slowly. This helps soil stay fertile and helps plants grow for a long time.
These changes help soil stay strong when it is dry. They also help soil keep water and nutrients for plants. Better soil helps roots grow well and makes soil healthier.
Chemical Effects on Soil
Ammonium humate changes the chemicals in soil. Its humic acids mix with soil minerals and nutrients. The effects depend on the kind of clay in the soil. The table below shows how humic acid coatings, like ammonium humate, change cation exchange capacity (CEC) and ammonium ion holding:
Clay Mineral | Effect of Humic Acid (HA) Coating on CEC | Effect on Ammonium (NH4+) Adsorption and Fixation |
|---|---|---|
Montmorillonite | CEC and SSA go down a lot | Holds more cations and likes NH4+ more |
Illite | CEC and SSA go down a little | Holds fewer cations and less NH4+ |
Kaolinite | CEC goes up a little | Holds more cations and likes NH4+ more |
Humic substances in ammonium humate help soil keep nutrients by joining with metals and ions. This makes more nutrients ready for plants and helps soil stay fertile. Even though we do not know much about its effect on soil pH, ammonium humate helps balance soil chemistry and helps nutrients move in soil.
Biological Activity
Ammonium humate helps living things in soil grow. Its humic parts help good bacteria like Chloroflexi, Acidobacteria, and Actinobacteria. These bacteria break down old plants and help move nutrients. More bacteria means better soil and stronger roots.
Humic acids in ammonium humate also make soil enzymes work better. Enzymes help get nutrients from old plants and make them ready for new plants. This helps nutrients move in soil and keeps soil healthy. By helping both bacteria and enzymes, ammonium humate makes soil stronger and helps farms last longer.
Tip: Using ammonium humate often can help soil stay fertile, make soil better, and help crops grow well for many years.
How Ammonium Humate Works in Soil
Nutrient Uptake
Ammonium humate helps crops take in more nutrients. When it is put in soil, it makes H+-ATPase enzymes in roots work harder. These enzymes make a proton gradient. This gives energy to move nutrients like nitrate into plants. Crops get more nitrogen this way. Nitrogen is very important for plants to grow and make more food.
Humic substances in ammonium humate help roots grow and turn on enzymes like nitrate reductase, glutamate dehydrogenase, and glutamine synthetase. These enzymes help plants use nitrogen better.
The humic content also helps plants with both main and extra metabolism. This makes plants stronger and helps them handle stress.
How well humic substances work depends on how and when they are used. Using them the right way helps crops get the most nutrients.
In carrots, using ammonium nitrate and potassium humate together when water is low helped plants take in more potassium, magnesium, zinc, and calcium. This also helped plants use water better and grow more food.
Better nutrient uptake helps plants do photosynthesis and build strong cell walls. This keeps plants healthy and helps them grow more.
These changes help crops use nutrients better. This means more food and better soil.
Soil Particle Aggregation
Humic substances in ammonium humate help soil particles stick together. This makes stable groups called aggregates. This process is called flocculation. It lowers soil bulk density and makes more spaces in the soil. Roots can grow easier and water and air move better.
Humic acid in the humate makes loose soil clump together. These clumps stay strong even when wet.
Studies show soil aggregates can go up by 1.5 to 3 times. Water-stable aggregates can rise by 8.5% to 30% after using humate.
Better aggregation helps soil keep water and nutrients. This stops them from washing away.
Humic substances join with metal ions and nutrients. This keeps them ready for plants to use and helps crops grow more.
More types of microbes and special soil proteins work with humic substances to make soil clumps even stronger.
Better soil structure from humate means roots have a good place to grow. This makes plants stronger and helps them make more food.
Stress and Disease Resistance
Ammonium humate helps crops fight stress and diseases in soil. The humic content turns on plant defenses by helping plants take in and use nutrients. It also starts other plant processes that help with stress from things like drought, salt, or disease.
Humic substances in humate turn on antioxidant enzymes like peroxidase, catalase, and phenylalanine ammonium lyase. These enzymes protect plant cells from stress damage. The humic content also affects signals like nitric oxide and calcium ions. These signals help plants deal with stress.
Spraying humic substances on leaves helps plants grow and makes more green color in leaves. This gives plants extra protection from stress. The many chemicals in humic substances help soil keep water and balance changes. This helps plants grow and make more food even when conditions are hard.
Ammonium Humate in Saline-Alkali and Alkaline Soils
Ammonium humate works well in salty and alkaline soils. Regular fertilizers do not work as well in these soils. Organic fertilizers like ammonium humate add more organic matter, nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium to soil. They also lower soil pH by reacting with alkaline parts. This makes nutrients easier for plants to use.
In field tests, crops with ammonium humate fertilizer grew better than those with only chemical fertilizer. For example, maize yield went up by almost 49% with organic fertilizer. In rice, using ammonium humate with less chemical fertilizer made plants healthier, gave more panicles, and raised yield by over 6% compared to full chemical fertilizer.
These results show humate helps soil and crops, even in tough soils. Better nutrient cycling, more soil enzyme activity, and better water holding all help plants grow and make more food.
Note: Ammonium humate is a good choice for farmers with salty or alkaline soils. Its humic content and balanced nutrients help keep soil healthy and grow more crops.
Application and Use
Methods of Application
Farmers use different ways to put ammonium humate on crops. The most common way is to add it right to the soil. They spray or mix the product into the ground. Tests on sandy soil show this works best. Using the AH2 form in soil gives more crops and healthier dirt than spraying on leaves. Putting it in the soil adds more big nutrients and organic matter. In greenhouses, growers put humic acid in the soil to help plants grow bigger and get more nutrients.
Other ways to use ammonium humate are:
Foliar spraying: This means spraying the solution on plant leaves. It helps but is not as good as putting it in the soil.
Seed treatment: This means covering seeds with humic substances before planting. It helps roots start growing early.
Fertigation: This means mixing humic products with water for watering. It spreads the product evenly in the soil.
Note: Putting ammonium humate in the soil is the best way to help crops grow and make soil better in fields and greenhouses.
Suitable Crops and Soils
Ammonium humate can be used for many crops and soils. Farmers use it for grains, vegetables, fruits, and oilseeds. Crops like wheat, maize, rice, and potatoes grow better with humic products. In salty or alkaline soils, ammonium humate helps crops handle stress and grow more. Sandy soils hold more water and nutrients with humate. Heavy clay soils get better structure and roots grow stronger.
The table below lists crops and soils that work well with ammonium humate:
Crop Type | Suitable Soil | Application Benefit |
|---|---|---|
Wheat | Sandy, saline, loam | Higher yield, better roots |
Maize | Alkaline, sandy | More biomass, strong crop |
Rice | Clay, saline | Improved yield, stress aid |
Vegetables | Loam, sandy | Better quality, growth |
Potatoes | Sandy, loam | Higher yield, nutrient use |
Tip: Ammonium humate works in most soils, but testing soil first helps pick the right amount for each crop.
Dosage and Timing
Using the right amount and timing is important for ammonium humate. Tests show that using more humic products can help crops grow and get more nutrients. For soil, experts say to use 5–10 kg per hectare for most crops. In greenhouses, growers use 0.5–2 g per liter of water.
Put ammonium humate on before planting or when crops are just starting to grow. Use it again at important times, like when wheat starts to grow more stems or when vegetables start to flower. Do not use too much, because extra humic product may not help more.
Use in wet soil for best results.
Mix with other fertilizers to help plants take up more nutrients.
Change the amount you use based on soil, crop, and local needs.
Callout: Using ammonium humate often helps crops grow strong, gives more food, and keeps soil healthy for a long time.
Crop Productivity Benefits
Yield Improvement
Ammonium humate helps crops grow more food. Farmers see bigger harvests when they use it. The humic content makes roots grow deeper and stronger. This helps plants get more water and nutrients. Crops then grow better and give more food. In tests, crops with ammonium humate had higher yields than those without it. Wheat and maize fields made more grain per acre. Potato farmers got bigger potatoes and more even harvests. Humic substances give out nutrients slowly all season. This helps crops grow well from start to finish. Yields stay high and crops do better.
Tip: Using ammonium humate often helps keep yields high, even in tough soils.
Quality Enhancement
Farmers want crops that look and taste good. Ammonium humate helps with this too. Crops grown with humic products have brighter color and firmer texture. They also have more vitamins and minerals. Carrots and potatoes taste better and last longer. Fruits are sweeter and look nicer. Humic substances help crops take in trace minerals from soil. This makes the harvest healthier. Better soil from humic use means stronger roots and less disease. Crops look better and keep longer after picking. Better crops sell for more money and help farmers earn more.
Research and Case Studies
Recent studies show ammonium humate helps crops a lot. Scientists tested it on potatoes with potato virus Y. They found that spraying ammonium humate made leaves greener and stems longer. Plants were healthier and gave more food. Crops with ammonium humate took in more nutrients and fought off virus damage. This means humic products help crops grow even when stressed.
Other research mixed humic acids with amino acids. These mixes help plants grow faster and fight drought and disease. Crops used more nutrients and grew stronger. Farmers using these products saw higher yields and better crops. These results show ammonium humate helps farms grow more food and use fewer chemicals.
Benefit | Effect on Crop Productivity |
|---|---|
Higher yield | More harvest per acre |
Better quality | Improved taste, color, nutrition |
Stress resistance | Stable yield in tough conditions |
Sustainable agriculture | Less need for chemicals |
Note: Ammonium humate is a proven way to help crops grow more, look better, and stay healthy on today’s farms.
Safety and Environmental Impact
Environmental Safety
Ammonium humate is safer than many chemical fertilizers. It comes from natural sources and breaks down in soil. It does not leave behind anything harmful. Many farmers and gardeners pick ammonium humate for healthy soil. Microbes and earthworms do well when it is used. Ammonium humate helps soil keep water and nutrients. This means less runoff and cleaner rivers.
Experts say ammonium humate does not build up in nature. It makes soil structure better and keeps soil healthy for a long time. Because it is organic, it works well with green farming. People who use ammonium humate help the earth and keep soil good for the future.
🌱 Ammonium humate helps the environment by making soil better and lowering pollution.
Limitations and Risks
Ammonium humate is mostly safe, but there are some limits. The quality can change depending on where it comes from. Some products may have bad minerals or heavy metals if not made right. Farmers should read labels and buy from trusted sellers.
Using too much ammonium humate can mess up soil nutrients. Plants might not grow well if there is too much nitrogen. Using too much can also cause nutrients to wash away, especially in sandy soil. People should use the right amount and test soil before using a lot.
Ammonium humate works best with good soil care.
It does not take the place of balanced fertilizer.
Some soils may not work as well, especially if they already have lots of organic matter.
Regulatory Aspects
In the U.S., ammonium humate is part of the National Organic Program. The USDA manages this program. In 2001, the National Organic Standards Board said humic acids, including ammonium humate, could be used in organic farming. This means farmers can use ammonium humate on organic farms. The USDA gives reports and reviews to support this.
Other groups like the EPA and FDA have strict rules for chemical fertilizers. These rules make people want to use natural products like ammonium humate. Humate products are getting more popular in organic farming because they are natural. But there are still problems with making sure all products are the same. The National Organic Program gives labels and certificates for organic products. Ammonium humate is still being checked for more uses.
Note: Federal support and easier rules for organic products help ammonium humate become more common in farming. Farmers should pick certified products to make sure they are good and follow the rules.
Ammonium humate is special because it helps soil in many ways. It makes soil stronger and helps good microbes grow. Plants can get more nutrients from the soil. Farmers and gardeners notice more crops and better plants when they use it often. Some main benefits are:
More helpful microbes and better enzyme work
Soil holds water better and stays together
Shoots and seeds have more nutrients
Plants give more food and handle stress better
To get the best results, try it on a small area first and watch how your plants do. Ask a local expert for advice that fits your farm or garden. Scientists keep studying how to use it best for different soils and crops.
FAQ
What is the best way to apply ammonium humate?
Farmers put ammonium humate right into the soil. They can also mix it with water for irrigation or spray it on leaves. Putting it in the soil works best for most crops.
Can gardeners use ammonium humate for home plants?
Yes, gardeners can use ammonium humate for vegetables, flowers, and lawns. It makes soil better and helps plants grow strong. Always use the amount shown on the label.
Is ammonium humate safe for the environment?
Ammonium humate comes from natural things. It breaks down in soil and does not hurt water or animals. Many experts say it is good for green farming.
How does ammonium humate help plants during drought?
Ammonium humate helps soil keep more water. Plants use this water when it is dry. Roots grow deeper, so plants can live through drought.
Does ammonium humate replace regular fertilizer?
No, ammonium humate does not take the place of regular fertilizer. It works best when used with other fertilizers. Farmers use both to help soil and get more crops.
What crops benefit most from ammonium humate?
Wheat, maize, rice, potatoes, and many vegetables do well with ammonium humate. It works in sandy, clay, and salty soils. Farmers get more crops and better plants.
How often should farmers apply ammonium humate?
Farmers use ammonium humate when planting and at important times as crops grow. They may use it again every few weeks for best results. Always check soil and crop needs before using more.
Can ammonium humate help with soil salinity?
Yes, ammonium humate helps salty and alkaline soils. It adds organic matter, balances pH, and helps crops get nutrients. Many farmers use it to fix poor soils.
See Also
Understanding Humate Soil Conditioner And Its Functionality
How NPK Fertilizer With Humate Enhances Plant Growth
Exploring Sodium Humate Uses And Benefits In Vietnam
Comparing Sodium Humate And Additives For Aquaculture Success
